Abstract
242340
Introduction: The small molecule radiotherapeutic agent 177Lu-PSMA-617 (Pluvicto®) targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), an exceptional biomarker for prostate cancer, was recently approved by the FDA for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Small molecule PSMA-binding agents localize to salivary glands, which can be a significant source of off-target toxicity. In contrast, PSMA-targeting antibody-based constructs (e.g., 177Lu-DOTA-J591) do not localize significantly to the salivary glands but have been shown to suffer from different dose-limiting toxicity challenges, likely due to a low blood clearance rate. The present study describes use of a minibody derivative of J591 (IAB2MA) to increase the clearance level and a recently developed macrocyclic chelator (L804) that can be labeled with Lu-177 and Zr-89 at room temperature, toward developing safer and more efficacious radiotherapeutic treatment options for prostate cancer.
Methods: L804 was compared to the current gold standard chelators DOTA and DFO conjugated to the J591-derived PSMA-directed IAB2MA minibody for radiolabeling with Lu-177 and Zr-89 in preclinical biodistribution, imaging, dosimetry using two methods (organ-level (MIRDcalc) and voxel-level based (Imalytics) dose calculations), and efficacy studies in a PSMA-positive PC3-PIP tumor-bearing mouse model of prostate cancer.
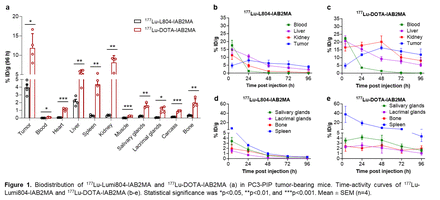
Results: Quantitative radiolabeling of the L804-IAB2MA construct with Lu-177 or Zr-89 was achieved at ambient temperature under 30 min at a molar activity of 18.5 or 9.25 MBq/nmol, respectively with >99% radiochemical yield, which is comparable to the DFO-IAB2MA construct with Zr-89. In contrast, DOTA-IAB2MA was radiolabeled with Lu-177 for 30 min at 37 °C and only ~90% radiochemical yield could be obtained. Results from in vivo studies showed a significantly lower accumulation of radioactivity in tumors of PC3-PIP tumor-bearing mice following treatment with 177Lu- and 89Zr-L804-IAB2MA compared to 177Lu-DOTA-IAB2MA and 89Zr-DFO-IAB2MA, respectively, likely due to more rapid blood clearance of the L804 conjugates (Fig. 1). After 72 h, accumulation of 177Lu-DOTA-IAB2MA and 89Zr-DFO-IAB2MA was significantly higher in all organs examined (i.e., heart, liver, spleen, kidney, muscle, salivary glands, lacrimal glands, carcass, and bone) compared to 177Lu- and 89Zr-L804-IAB2MA, consistent with higher recovered activity in the urine/feces for the L804 agents (Figs. 1a). SPECT/PET/CT imaging data showed no significant difference in SUVmean of the tumors or muscle between the radiotracers, although there is a consistent trend towards higher SUV for 177Lu-DOTA-IAB2MA in both tissues compared to 177Lu-L804-IAB2MA (Figs. 2a-d). Dosimetry analysis indicated significantly higher absorbed doses of 177Lu-DOTA-IAB2MA in tumor, kidney, liver, and muscle compared to 177Lu-L804-IAB2MA. MIRDcalc and Imalytics generated comparable dosimetry results (Fig. 2e). PC3-PIP tumor-bearing mice treated with single doses of 177Lu-L804-IAB2MA (18.4 or 22.2 MBq, median survival > 75 days) exhibited significantly prolonged survival and reduced tumor volume compared to unlabeled minibody control (median survival = 44 days, Fig. 2e). No significant difference in survival was observed between groups of mice treated with 177Lu-L804-IAB2MA or 177Lu-DOTA-IAB2MA (18.4 or 22.2 MBq), although the percent survival of the lower dose (18.4 MBq) 177Lu-L804-IAB2MA group was lower than that of the DOTA agents (18.4 MBq or 22.2 MBq). Treatments with 177Lu-L804-IAB2MA resulted in lower absorbed doses in tumors and less toxicity than that of 177Lu-DOTA-IAB2MA (Fig. 2e). CBC analysis showed a more pronounced depletion and slower recovery of leukocytes and lymphocytes following treatments with the DOTA agent.
Conclusions: The stably chelated 177Lu-L804-minibody conjugate is a promising agent for improving radiotherapeutic treatments of prostate cancer.