Abstract
242240
Introduction: Toward achieving high resolution and sensitivity simultaneously, the Provision-PET was designed using a four-layer dual-ended readout PET detector with fast Lutetium Fine Silicate (LFS) scintillating crystals and electronics, enabling depth of interaction and time-of-flight identification capabilities. Each layer includes eight crystals (2.05×30×4.4mm), with independent readout including 4 strip SiPMs attached to opposite sides of the layer (Figure 1A). The independent readout of the layers enables identification of the Compton scattered events between layers. A number of methods have been proposed for identification of the first interaction layer (FIL), mostly based on Compton and Klein-Nishina equations. However, they are rarely applicable due to their computational demand. In this study, we evaluated the accuracy of three easily applicable methods for the Provision module using Monte Carlo simulations.
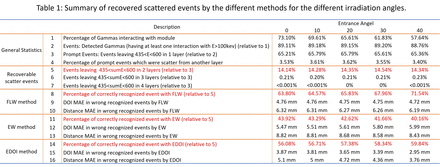
Methods: Provision PET module was simulated in GATE (Geant4 application for tomographic emission) toolkit. The front surface of the module was irradiated with 511 keV photons, uniformly with incident angles (with normal vector of detector) of 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 degrees, until 1 million photons are detected for each. A threshold of 100 keV energy deposition in a single layer was assigned to the detector for recording an event, considering practical limitations. The energy resolution was set to 10% with 511 keV as reference, and a window of 425-600 keV was considered for analyzing events (whether the energy is deposited in a single layer or summation of deposited energies in multiple layers). For scattered event recovery, only events which activated two layers were considered to-be-recovered (TBR). TBR scattered events follow 4 scenarios including forward and backward scattering with different energy deposition between the layers (Figure 1B). Three simply applicable methods were applied to detect the FIL: 1) FLW method: selecting the front layer as the winner; 2) EW method: selecting the layer with maximum deposited energy; and 3) E-DOI method: while L1 is the front layer and L2 is the deeper one, L1 is the FIL, if (DOI1-DOI2)(E1-E2) is positive, and otherwise, FIL is L2.
Results: Prompt events detected in a single layer within the energy window [425-600] keV formed ~65% of the events. Among these, 3.5% gave the wrong location since they were initially scattered in other layers with low energy deposition (below 100 keV detection threshold of the module). Relative to prompt events, a sensitivity gain of ~14.3% can be achieved by detecting scattered events activating two layers (TBR events), and only ~0.2%, and <0.001% increase in sensitivity were observed when events with 3 and 4 activated layers were recovered. FLW, EW, and EDOI methods, respectively, identified FIL correctly with ~66.7%, ~42.3%, and 57.7% accuracy. Wrong recovered events (wrong FIL) had a DOI mean absolute error (MAE) of ~4.75, ~5.6, 3.4 mm, and Euclidean-distance MAE of ~6.2, 8.6, and 4.5 mm for FLW, EW, and EDOI methods, respectively (Table 1). Figure 1C shows the scatter plots of ΔDOI vs. ΔE for when the front layer is the FIL and when it is not. The whole analysis was repeated via assigning no energy blurring in simulation; however, the results did not differ significantly.
Conclusions: A 14.3% sensitivity gain can be achieved by detecting the scattered events which can be translated into 14% reduction in injected activity (or patient dose). FLW method showed the best accuracy in detecting FIL. EDOI method although showed lower accuracy for detecting the FIL revealed lower MAE for both DOI and Euclidean distance. By reducing the energy threshold for detecting events, not only more scattered events can be recovered but also the wrong-located prompt events can be identified and corrected. Experimental implementation of the methods is under progress.