Abstract
242155
Introduction: Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) employing 177Lu-DOTATATE is a promising and well-tolerated treatment for neuroendocrine tumors, albeit with recognized potential for inducing a decline in renal function. This study aims to quantify absorbed dose (AD) to kidneys and evaluate its association with renal function assessed by the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at 9 months after the completion of the final PRRT cycle.
Methods: Patients who completed four (7.4 GBq/cycle) cycles of 177Lu-DOTATATE with renal protective amino acids, underwent multi-timepoint SPECT/CT imaging after each cycle, and had follow-up labs up to 9 months after the last cycle were included in this study. The eGFR at baseline and 9 months was estimated using the CKD-EPI formula. Dosimetry was performed for each cycle using an automated workflow encompassing SPECT-SPECT co-registration, Monte Carlo-based voxel dosimetry, and absorbed dose-rate fitting/integration. The renal AD was calculated as the weighted average of left and right kidney segmented using a deep learning model. Univariate and multivariable models were used to assess the association between the eGFR at 9 months and the predictors: kidney AD (both cycle 1 and cumulated over all cycles) and baseline eGFR.
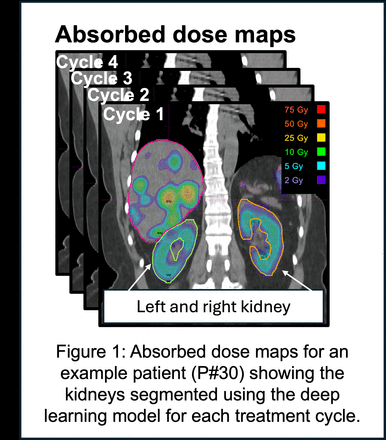
Results: A cohort of 24 patients were administered with a median [range] cumulative activity of 29.2 [15.2–30.7] GBq. A reduction in eGFR was evident, decreasing from 81.1 [54.8–119.4] mL/min/1.73m2 at baseline to 72.2 [37.4–108.1] mL/min/1.73m2 at 9 months post-last treatment cycle. Renal toxicity CTCAE v5.0 Grade changed from 1 to 2 for 2/24 patients, while no Grade 3 or higher toxicity was observed. The median [range] cycle 1 and cumulative (across 4 cycles) kidney AD were 3.5 [1.5–6.6] Gy and 14.6 [7.6–25.3] Gy respectively (Fig1). In unvariate analysis, a significant positive association (adjusted R2 = 0.57) was observed between 9-month eGFR and baseline eGFR, while a significant negative association was found between 9-month eGFR and cycle 1 kidney AD (adjusted R2 = 0.29) and cumulative kidney AD (adjusted R2 = 0.26). The multivariable model, including both baseline eGFR and cycle 1 kidney AD as predictors, resulted in an improved adjusted R2 of 0.64. Similarly, the multi-variable model including baseline eGFR and cumulative kidney AD resulted in an adjusted R2 of 0.65 (Fig2). The interaction term of baseline eGFR and AD was excluded from the multivariable model due to its lack of statistical significance. The parameter estimates of the described models are presented in Table 1.
Conclusions: PRRT with 177Lu-DOTATATE induces a mild deterioration in renal function; however, no instances of Grade 3 or 4 renal toxicity were observed up to 9 months post-treatment. A significant association was observed between eGFR at 9 months and both cycle 1 and cumulative renal AD. In a multi-variable model, one mL/min/1.73m2 increase in baseline eGFR was associated with a 0.63 mL/min/1.73m2 increase in eGFR at 9 months, and one Gy increase in cumulative renal AD was associated with a 1.25 mL/min/1.73m2decrease in eGFR at 9 months.