Abstract
241946
Introduction: In SPECT Myocardium Perfusion Imaging (MPI), gastrointestinal (GI) activities tend to add scattered photons into the inferolateral walls, preventing the accurate diagnosis and interpretation of MPI images, and thus scatter correction is particularly important for patients with high GI uptake in the background. Considering the success of direct deep learning-based attenuation correction (DL-AC), we aim to develop a direct deep learning-based attenuation and scatter correction (DL-ASC) solution, demonstrating the clinical value of DL-ASC.
Methods: We collected 400 subjects of 99mTc sestamibi SPECT MPI studies acquired in a GE Discovery NM/CT 570c scanner. Both CT-based attenuation corrected (CTAC) and attenuation and scatter corrected (ASC) images were reconstructed using the vendor provided software (Xeleris). A UNet-like network combined with residual blocks was developed and trained for generating DL-ASC images directly from non-corrected (NC) images in the image space, without undergoing an additional image reconstruction step. The same network was trained to predict DL-AC images for comparison to show clinically meaningful differences between DL-AC and DL-ASC. The performance of DL-ASC was evaluated by the normalized mean square error (NRMSE), peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), and structural similarity index (SSIM). Statistical analyses were performed using joint histograms, demonstrating voxel-wise correlation between DL-ASC and ASC. The clinical value of DL-ASC was illustrated through the comparison of polar maps.
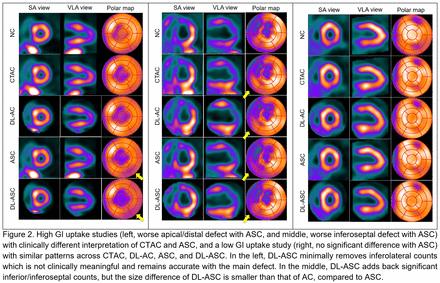
Results: Compared to the reference ASC, the DL-ASC achieved the NRMSE of 0.1245 ± 0.033, the PSNR of 22.4 ± 2.14, and the SSIM of 0.895 ± 0.029, whereas DL-AC obtained the NRMSE of 0.1822 ± 0.043, the PSNR of 19.1 ± 2.03, and the SSIM of 0.854 ± 0.026. These results are consistent with the joint histogram of ASC versus DL-ASC (slope = 0.98, R2 = 0.96) which shows more correlation than that of DL-AC versus ASC (slope = 0.97, R2 = 0.94). In qualitative comparison, for studies with high GI uptake close to the myocardium, DL-AC shows clinically different interpretations from ASC, whereas DL-ASC indicates no meaningful clinical differences, or a significant but small difference compared to ASC. Additionally, in studies with low GI uptake, both CTAC and ASC show mostly similar uptake patterns, as does DL-ASC.
Conclusions: We investigated the feasibility of joint correction of attenuation and scatter through deep learning for SPECT MPI, demonstrating the clinical value of DL-ASC. DL-ASC can facilitate the use of scatter correction for patients with high GI uptake in dedicated cardiac SPECT systems.