Abstract
241874
Introduction: Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke that results from the disruption of cerebral blood flow, causing neuronal death, neuroinflammation, and other cerebral damage. Several studies indicated that the abnormal expression of Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) was observed in experimental stroke animal models. Inhibition of HDAC6 has been found to have neuroprotective effects in animal models of ischemic stroke. HDAC6-selective inhibitors exhibited therapeutic potential for ischemic stroke that can reduce infarct size, improve neurological function, and promote neurogenesis by inhibiting apoptosis, promoting neuronal survival, reducing neuroinflammation, and improving blood flow in experimental stroke models. Here, we aim to investigate the dynamic change of HDAC6 in the brain after ischemia in mice and evaluate the neuroprotective potential of our newly developed HDAC6 inhibitors in ischemic stroke mouse model using positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in vivo and histopathological analysis in vitro.
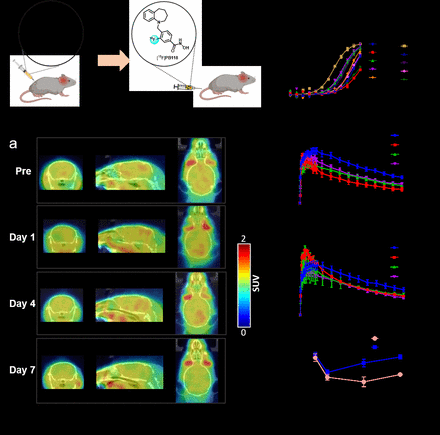
Methods: PET imaging studies with HDAC6-specific radioligand [18F]PB118 in mice with middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) surgery at different time points to monitor the dynamic change of HDAC6 after ischemic. A series of novel brain-permeable HDAC6 inhibitors were designed and prepared for the treatment of MCAO mice. The therapeutic potential of the most potent HDAC6 inhibitor, PB131, was evaluated by PET imaging studies with HDAC6-specific PET radioligand [18F]PB118 and 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO)-specific radioligand [18F]FEPPA.
Results: PET imaging with [18F]PB118 in an experimental model of MCAO revealed a dramatic decrease in uptake of [18F]PB118 in the ischemic hemisphere on the first day after the onset of ischemia, which mainly results from neuronal death. Although there was a slight increase of radioactivity in the ipsilateral hemisphere on the subsequent day 4 due to the reduction of ischemia and neuron restoration, the uptake of [18F]PB118 remained at a lower level on day 7. A trend of elevation of [18F]PB118 in the contralateral hemisphere, indicating that local ischemia can cause HDAC6 expression in the whole brain. In vitro immunohistofluorescence staining experiments on HDAC6 expression detection are consistent with PET imaging findings. Medication with PB131 alleviated the decline in radioactivity uptake of [18F]PB118 and significantly reduced the infarct size in MCAO mice. Furthermore, PET imaging studies with [18F]FEPPA for TSPO demonstrated that dramatically reduced uptake of [18F]FEPPA was observed in PB131-treated MCAO mice, suggesting the anti-neuroinflammation effects of PB131 by immune response regulation.
Conclusions: We revealed the dynamic change of HDAC6 in ischemia in a non-invasive way in living animals, and our newly developed HDAC6 selective inhibitor PB131 could serve as an effective neuroprotective agent for ischemic stroke. These findings furnish new considerations for the design of future ischemic stroke therapeutic strategies.