Abstract
241838
Introduction: Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is overexpressed on the surface of tumor cells and inhibits the activity of T cells by binding to programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) on the surface of immune cells. Antagonists targeting PD-L1 can inhibit the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction, thus blocking the tumor immune escape pathway and maintaining the tumor killing activity of T cells. Of note, peptide imaging tracers targeting PD-L1 have shown promising results in tumor diagnosis. We previously reported D-peptide—based tracers [64Cu/68Ga]DPA with excellent in vivo stability and pharmacokinetics1. The multimeric peptides can help improve tumor-targeting efficacy and generate higher-quality in vivo imaging. This strategy has been widely used in the development of multimeric Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptides. In this study, we designed and synthesized the dimer tracer DP2 and the trimer tracer DP3 based on the precursor DPA, and radiolabeled with 68Ga to evaluate their in vivo performance to monitoring PD-L1.
Methods: DP2 and DP3 were synthesized based on DPA and radiolabeled with 68Ga. PET/CT imaging of 68Ga-DP2 and 68Ga-DP3 was performed in tumor bearing mice model to visualize the radioligand distribution in vivo. The dynamic changes of radioactive tracers in normal mice were monitored with dynamic PET. Preclinical pharmacokinetics and tumor uptake of 68Ga-DP2 and 68Ga-DP3 in normal and tumor mice were determined by biodistribution assay. Cellular uptake and competitive binding assay of 68Ga-DP2 and 68Ga-DP3 were performed. Stability of both compounds was tested in vivo and in vitro.
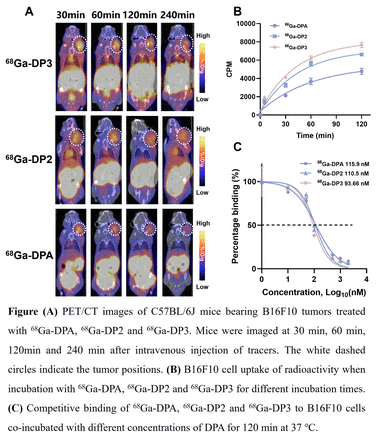
Results: 68Ga-DP2 and 68Ga-DP3 were stabilized in phosphate buffered saline and mouse serum for 2 h. PCT/CT imaging showed that both 68Ga-DP2 and 68Ga-DP3 showed significantly increased tumor uptake and retention compared with monomer 68Ga-DPA. The tumor uptake in 68Ga-DP3 group was higher than that in 68Ga-DP2 group. Studies on the biological distribution of 68Ga-DP3 in tumor bearing mice further confirmed that the tumor uptake of 68Ga-DP3 was higher than 68Ga-DP2. Compared with 68Ga-DPA, the uptake of 68Ga-DP2 and 68Ga-DP3 was time-dependent and the uptake value was higher. The binding affinity of 68Ga-DP3 (93.66 nM) was better than 68Ga-DP2 (110.5 nM) and 68Ga-DPA (115.9 nM). Dynamic PET and normal mouse biological distribution showed that 68Ga-DP2 and 68Ga-DP3 were taken up by the kidneys and rapidly cleared from the blood and other non-specific organs.
Conclusions: 68Ga-DP2 and 68Ga-DP3 were successfully synthesized and radiolabeled with high radiochemical purity and stability. 68Ga-DP3 has increased tumor uptake and retention properties compared with 68Ga-DPA. Thus, the use of polymeric structures could be the next step towards prolonged uptake of PD-L1 inhibitors.