Abstract
241820
Introduction: The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) is a transmembrane kinase receptor expressed on the vascular and lymphatic endothelium, which is critical for the proliferation/migration of vascular endothelial cells via VEGF signalling. Meanwhile, growing evidence has demonstrated that VEGFR-2 is an overexpressed biomarker in different kinds of cancer, namely breast cancer, cervical cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, renal carcinoma, and likewise. Therefore, we reasonably chose VEGFR2 as the target of imaging which can provide useful information for cancer diagnostics and optimize anticancer therapy. Thus, our goal is to develop more efficient, durable, and safer radiotracers based on peptides for PET imaging of VEGFR2 in various cancers.
Methods: VEGF-P3(NC), a documented peptide with a reported KD value of 49 nM, contains three Methionines. Based on the sulfonium crosslinking method, we changed the quantity of Methionine in the sequence to obtain peptides V2-V5. Then, we used linkers to connect the Methionine side chain at different distances under controlled conditions, achieving precisely form the cyclic peptides [denoted M2-M5]. Next, M2-M5 were conjugated with DOTA and labelled with Cu-64. [64Cu]Cu-[M2-M5] was used for small-animal PET of mice bearing U87MG human glioblastoma cells. Then, flow cytometry analysis and microscopy studies were performed to compare the VEGFR-2 binding affinity of VEGF-P3(NC), M2 and DOTA-M2 in U87MG, B16F10 and A549 cell lines. Biodistribution studies, autoradiography and immunofluorescence staining were performed to confirm the noninvasive imaging results.
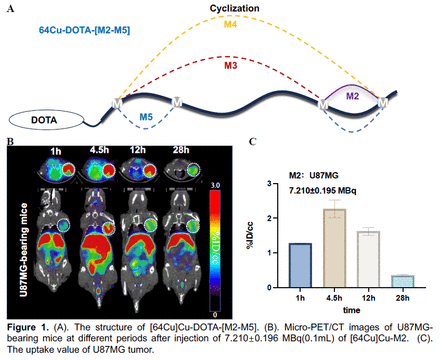
Results: M2-M5 were obtained with appropriate yield. Radiolabeling of M2-M5 with 64Cu achieving high yield and specific activity. Radiotracers showed significantly varied stability in mouse serum. [64Cu]Cu-M2 rapidly accumulated within U87MG tumours in Balb/c mice, enabling successful PET imaging of tumors at 1-hour post-injection (i.v.). The calculated tumor uptake values were 4.27%ID/g, reaching a peak value of 6.56 %ID/g at 4.5 hours. The modification of the Methionine side chain significantly extended the tracer’s retention in the tumor sites. Until 12 hours post-injection, the uptake value remained at 4.62 %ID/g. Additionally, M2 and DOTA-M2 exhibited significant affinity for U87MG and B16F10, while showing low affinity for A549.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that Met-based sulfonium tethering is a viable strategy to improve radioactivity uptake and retention of a VEGFR2 targeting radiotracer. Therefore, [64Cu]Cu-M2 is a promising, clinically translatable PET tracer for the noninvasive quantification of VEGFR2 in vivo. It is anticipated as a therapeutical radiopharmaceutical radiolabeled with 177Lu.