Abstract
241739
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer. To date, the imaging of HCC is difficult, challenging for disease staging (especially for extrahepatic disease) and barely improved over the past decades. Glypican-3 (GPC3) is a cell-surface receptor highly expressed by HCC. Histopathologically, GPC3 is of both diagnostic and prognostic value, with GPC3-positive HCC having shorter disease free survival vs GPC3-negative HCC. GPC3 has been reported as a potential target for diagnosis and treatment of HCC for nuclear theranostics. RYZ-GPC3 is a DOTA modified macrocyclic peptide with high affinity for GPC3, which may allow PET imaging or nuclear therapy. Here we report initial clinical results of [68Ga]Ga-RYZ-GPC3 PET-imaging in patients with known or suspected HCC.
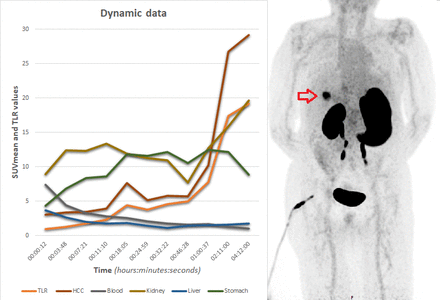
Methods: [68Ga]Ga-RYZ-GPC3 was obtained upon labeling the peptide precursor with 68Ga from a 68Ge/68Ga-generator and heating till 90⁰C for 10 min followed by sterile filtration. After administration of 2 MBq/kg [68Ga]Ga-RYZ-GPC3, a 60 min dynamic PET/CT scan (Siemens Biograph VISION) or (multiple longitudinal) static PET/CT (Siemens Biograph mCT or GE Discovery MI) were acquired between 45 minutes and 4 hours post-administration. Besides qualitative interpretation, standardized uptake values (SUVmax, SUVmean) were measured in various compartments using volumes-of-interest (VOI) corresponding to HCC lesions, non-tumor bearing healthy liver (HL), renal cortex, blood pool activity in the left ventricle (BP; at least 1 cm3 VOI) and gastric fundus. Additionally, tumor-to-healthy liver ratios (TLR) were calculated: SUVmean,HCC divided by SUVmean,HL, as an illustration of target-to-noise ratio.
Results: Radiolabeling to obtain [68Ga]Ga-RYZ-GPC3 was near quantitative, making the production highly reliable. Fifteen patients (five patients dynamic; ten patients static protocol) were scanned. One patient suspected to have HCC, did not have an HCC during follow-up. Another patient had a concurrent metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma, which did not show uptake, both qualitatively and quantitatively (SUV-values <1.0). Three HCC lesions in the same patient (with prostate cancer) were considered GPC3-negative as confirmed by immunohistochemistry; with heterogenous GPC3 expression within the HCC’s on PET/CT, illustrating disease heterogeneity. Majority of known, suspected, or indifferent HCC lesions showed uptake in qualitative assessment. In total, 38 HCC lesions were imaged at different time points, including the aforementioned GPC3-negative lesions. Mean SUVmax was 20.0 (range 2.7 - 95.3) and mean SUVmean was 10.2 (range 1.0 - 49.2) at 60 minutes. Uptake in HL and BP rapidly decreases over time and becomes negligible 45 minutes after administration (SUVmean <1.6), with a continuous declining trend till 4 hours after administration (Mean SUVmean = 1.0). The opposite occurs for HCC and TLR, which continuously increase up to 4 hours after administration (mean TLR 5.5 to 8.9 to 19.2, at 18 minutes, 1 hour and 4 hours post-injection respectively). In individual lesion analysis, TLR was the highest between 60 - 120 minutes post-injection. Uptake in the gastric fundus gradually increases in the first hour and decreases gradually afterwards (Mean SUVmean from 18.9 to 22.6, back to 14.9, at 18 minutes, 1 hour and 4 hours post-injection respectively).
Conclusions: [68Ga]Ga-RYZ-GPC3 is the first peptide based PET tracer that allows the high quality molecular imaging of HCC, with a rapid and favorable biodistribution. Thereby, [68Ga]Ga-RYZ-GPC3 is suitable for the selective diagnosis of HCC. In addition, based on the favorable biodistribution and in vivo dynamics on these diagnostic images, RYZ-GPC3 is very likely to hold therapeutic potential upon labeling with a therapeutic isotope (e.g 177Lu or 225Ac).