Abstract
241651
Introduction: As medical imaging technology advances, the diversity and quality of medical image continue to expand, leading to a growing demand for a quality assessment and utilizing images in multi-institutional applications. In response to this trend, cloud-based environments are emerging to enhance multicenter research in the field of medical imaging. Within these cloud platforms, federated learning promotes stable model development and robust image analysis, accommodating the diverse data quality contributed by various institutions and scanners.
This study introduces a cloud-based federated learning platform, which involves multiple institutions collaborating within a Kubernetes cluster as depicted in figure 1, with the aim of subtle 3D MRI segmentation for the striatal activity estimation for 18F-AV-133 VMAT2 PET images.
Methods: In this study, we hypothesize that three institutions, referred to as worker nodes, contribute their 3D brain MRI datasets sourced from 100 PPMI, 400 ADNI, and 200 GAAIN, respectively. These nodes are orchestrated within a Kubernetes cluster while maintaining physical isolation to ensure data privacy and security. A remote-control node within the cluster is responsible for aggregating models, each optimized by the respective worker nodes utilizing their datasets.
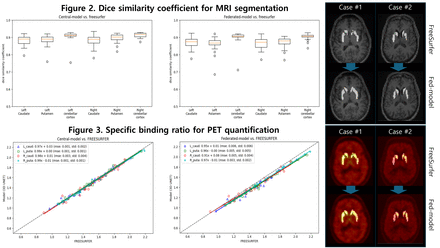
To train a segmentation model, T1-weighted brain MRI scans are processed by FreeSurfer to generate five binary masks, left and right caudate, putamen and the entire cerebellar cortex, serving as a reference for PET quantification. To evaluate federated model, dice similarity coefficient (n = 30) and specific binding ratio (n = 30) are calculated and compared with the results of FreeSurfer and software, respectively. Additionally, we validated its comparative performance with the centralized model, trained with collected multi-institutional data at a center.
Results: As shown in figure 2 (right) for caudate and putamen, the federated model demonstrated dice similarity coefficients comparable to FreeSurfer. Consequently, the specific binding ratio of 30 18F-AV-133 PET images from PPMI exhibited similar slopes to those obtained with FreeSurfer in figure 3 (right). When compared to the centralized model in figure 2 and 3 (left), the federated model maintained comparable performance, reflecting dice similarity coefficients and specific binding ratio that were on par with those of centralized model.
Conclusions: In this study, we implemented a 3D segmentation model on cloud-based federated learning platform. The federated learning model was well optimized in comparison to the centralized learning model. Moreover, its performance was comparable to that of the FreeSurfer software in terms of striatum segmentation and PET quantification.