Abstract
241605
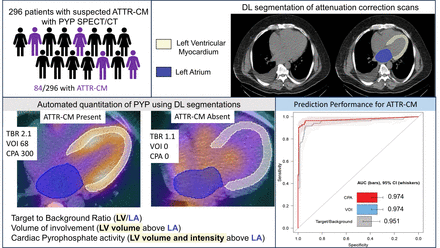
Introduction: Transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis (ATTR-CM) is increasingly recognized as a cause of heart failure in older patients, with 99mtechntium pyrophosphate (PYP) imaging frequently used to establish the diagnosis.Visual interpretation of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) images is the gold standard for interpretation but is inherently subjective. Manual quantitation of SPECT myocardial PYP activity is time-consuming and not performed clinically. We evaluated different methods for fully automated volumetric quantitation of PYP utilizing segmentation of co-registered anatomical structures from CT attenuation maps.
Methods: Patients who underwent SPECT/CT PYP imaging for suspected ATTR-CM were included. Diagnosis of ATTR-CM was determined using standard criteria. Cardiac chambers and myocardium were segmented from CT attenuation maps using deep learning, then transferred to registered SPECT images to quantify counts in left atrial blood pool and left ventricular myocardium. We evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of three methods for determining radiotracer activity: target-to-background ratio (TBR), cardiac pyrophosphate activity (CPA) and volume of involvement (VOI). We then evaluated their age-adjusted associations with the composite outcome of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization.
Results: In total, 296 patients were included, mean age 74.0 ± 12.0 years, with ATTR-CM diagnosed in 84 (28.4%) patients. Of the quantification methods, CPAand VOI had higher prediction performance for ATTR-CM (both area under the curve [AUC] 0.974, 95% CI 0.950 – 0.998) compared to TBR (AUC 0.951, 95% CI 0.917 – 0.985, p=0.002). Twenty-three patients ATTR-CM experienced cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization. Increasing CPA (hazard ratio [HR] 1.35, p=0.041), VOI (HR 1.34, p=0.046), and TBR (HR 1.58, p=0.039) were associated with an increased risk of events.
Conclusions: Deep learning segmentation of co-registered CT attenuation maps allows automatic quantification of hot-spot SPECT imaging such as PYP. This can be used to accurately identify patients with ATTR-CM and may play a role in risk prediction.