Abstract
241491
Introduction: Iomab-B (131I-apamistamab), a radioimmunoconjugate to anti-CD45, delivers high-dose targeted radiation to hematopoietic cells allowing for myeloablation and eradication of leukemic cells prior to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT). Very few patients with TP53 mutations are offered HCT because of the high post-HCT relapse and mortality for those patients. With better disease control and safer enabling of HCT due to its targeted delivery, Iomab-B led induction/conditioning can potentially improve outcomes even in pts with TP53 mutation. Here, we report the survival outcomes and dosimetric comparison of pts with and without TP53 mutations enrolled in the phase 3 SIERRA trial.
Methods: SIERRA (NCT02665065) was a multi-center, randomized, controlled phase 3 study. Patients 55 years or older with active R/R AML were randomized (1:1) to Iomab-B or conventional care (CC). Patients on the Iomab-B arm received Iomab-B with fludarabine and total body irradiation (2 Gy) followed by HCT. Pts on the CC arm received physician’s choice of salvage therapy. Patients achieving CR received physician’s choice conditioning and HCT, and those that did not were eligible to cross over (CO) to the Iomab-B arm. Patients received individualized doses of Iomab-B based on evaluation of organ-specific uptake and dosimetry estimates from gamma camera imaging following tracer dose administration, and as such organ dose estimates were available for every patient receiving Iomab-B.
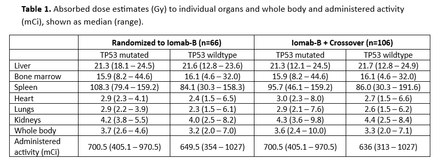
Results: Of 153 randomized pts, 66/66 (100%) who received the therapeutic dose in the Iomab-B arm underwent HCT vs. 14 (18.2%) in the CC group. Among evaluable pts, the primary endpoint of durable CR rates at 6 mos were 22% in theIomab-B group vs 0% in the CC group (95% CI;12.29, 34.73; p<0.0001). There were a total of 37 pts with TP53 mutations (CC=20; 131I-apamistamab=17) with a prevalence of 24.2%. The CR and dCR rates for Iomab-B treated pts were similar irrespective of TP53 mutation while in the CC group, no pts with TP53 mutation achieved CR or dCR. Table 1 shows the individual organ radiation dose estimates and administered activity comparing patients with mutated and wildtype TP53, illustrating no difference in the delivered radiation absorbed dose. The median overall survival (OS) for pts in the Iomab-B group, who were TP53 negative was 6.37 mos compared to 5.72 mos for those with TP53 mutation (HR=0.66; 95% CI [0.37, 1.18]; p=0.16). In the CC group (including CO pts). For patients with TP53 mutation who received Iomab-B (either through randomization or cross over), the median OS was 5.49 mos compared to a median 1.66 mos in pts who did not receive Iomab-B (CC without CO) [(HR=0.23; 95% CI [0.10, 0.52]; p=0.0002) (Figure 1)].
Conclusions: Patients with TP53 mutated relapsed/refractory AML have a dismal prognosis and are rarely offered alloHCT due to high post-transplant relapse rates.131I-apamistamab led alloHCT significantly improved survival in patients with TP53 mutations, similar to what is seen for patients without this mutation in terms of CR, dCR and survival. As delivered doses of this targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy were similar between patients with and without TP53 mutation, this suggests the mechanism of action of Iomab-B may overcome the negative impact of TP53 mutation in these patients. These data strongly support the use of 131I-apamistamab led induction and conditioning for alloHCT in relapsed/refractory AML even for patients with a TP53 mutation.