Abstract
241406
Introduction: The integrated positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (PET/MRI) system is commonly the preferred device in whole-brain imaging, which enable to provide precise anatomical and functional information with exceptional sensitivity and accuracy. However, it still suffers some limitations such as the radiation exposure risks and economic costs from radiopharmaceuticals. But the reduction of the injection dose may significantly affect the quality of brain PET images, resulting in increased image noise and decreased contrast. To decrease patient burden without sacrificing image quality, we introduced spatial brain anatomical alignment information for low-dose whole-brain PET and MR images to synthesize high-quality PET images.
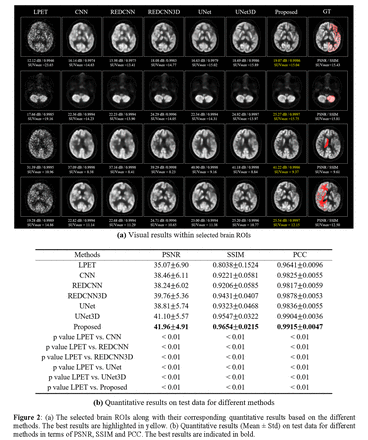
Methods: To improve the quality of low-dose whole-brain images, an adaptive 3D neural network with a spatial brain transform (SBF) module was proposed. Freesufer software was used to derive spatial brain anatomical alignment information, which was subsequently fused with low-dose PET and MR features through the SBF module. To assess the quality of the generated high-dose PET images, the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index measure (SSIM) and Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) were used for analyses. Moreover, the t test was also used for statistical analysis of the data from different brain regions. Furthermore, several deep learning methods, including CNN, REDCNN, REDCNN3D, UNet and UNet3D, were employed as comparison measures to evaluate the model performance. In addition to objectively assessing image quality with quantitative indicators, we performed volume of interest (VOI) analysis based on different brain regions to determine the standardized uptake value (SUV) distribution.
Results: Brain data were collected from 100 patients (23 males, 77 females). Both the visual and quantitative results showed that our approach achieved better model performance. The obtained PSNR and SSIM were 41.96 ± 4.91 dB (p<0.01) and 0.9654 ± 0.0215 (p<0.01), respectively, which, respectively achieved a 19% and 20% improvement compared with the original low-dose brain PET images. In comparison to the UNet3D model, which achieved the best quantitative results among other methods, had a PSNR of 41.10 ± 5.57 dB and an SSIM of 0.9547 ± 0.0322, which were still inferior to our method. The volume of interest (VOI) analysis of brain regions such as the left thalamus (PCC = 0.959) also showed that the proposed method could achieve a more accurate standardized uptake value (SUV) distribution while preserving the details of brain structures.
Conclusions: In this work, we have developed a 3D whole-brain image enhancement model combined with an SBF module to integrate PET-MR features and spatial brain anatomical alignment information, which achieved superior performance in accurate whole-brain PET image improvement. In future works, we attempted to apply our method to other multimodal systems, such as PET/CT, to assist clinical brain disease diagnosis and treatment.