Abstract
241401
Introduction: Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) encompasses a spectrum of disorders characterized by pulmonary alveolitis and interstitial fibrosis, comprising over 200 specific diseases. Except for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), some ILDs, despite regular treatment, manifest progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF), leading to heightened mortality. Early diagnosis of PPF is pivotal for prognosis; however, conventional imaging methods offer limited assistance in the early stages. Recent studies indicate that FDG PET/CT can unveil some information about ILDs. Furthermore, an emerging PET/CT tracer, the fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI), capable of targeting the up-regulated FAP in ILD, appears to be a promising diagnostic tool. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of FDG and FAPI PET/CT in ILD patients and determine their respective diagnostic value.
Methods: In a cohort of 97 patients with ILD, FDG and FAPI PET/CT were conducted within one week, assessing various PET/CT parameters. Kerbs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) and pulmonary function test (PFT) results within two months of PET/CT were documented. Follow-up included CT, PFT, and clinical symptom assessment after one year to differentiate between patients with PPF and non-PPF. Comparative analysis involved PET/CT parameters of both tracers, correlation assessments with KL-6 and PFT (FVC% and DLCOc%), and a comparison of PET/CT parameters between PPF and non-PPF groups, with ROC curve analyses.
Results: FDG and FAPI uptake were observed in the areas characterized by interstitial lung disease (ILD): 87% (85/97) of patients manifested both FDG and FAPI uptake, 8% (8/97) exhibited only FAPI uptake, 2% (2/97) showed only FDG uptake, and 2% (2/97) had neither FAPI nor FDG uptake. All PET/CT parameters in FAPI were significantly higher than the corresponding ones in FDG, especially the whole lung SUVmean (WL-SUVmean 1.04 [0.82-1.33] vs 0.82 [0.67-1.01], p<0.001). KL-6 was positively correlated with the WL-SUVmean of both FDG and FAPI PET/CT (rsp= 0.485**, 0.475**, respectively). WL-SUVmean in both FDG and FAPI were also negatively correlated with FVC% (rsp=-0.372**, -0.418**, respectively) and DLCOc% (rsp=-0.482**, -0.506**, respectively). All FAPI PET/CT parameters in PPF patients (n=19) were markedly higher than those in non-PPF patients (n=6), notably the WL-SUVmean (1.24 [1.04-1.42] vs 0.73 [0.58-0.80], p<0.001). The ROC curve for FAPI WL-SUVmean (cutoff = 1.01) to predict PPF was highly significant (AUC=0.9398, sensitivity=100%, specificity=89.47%).
Conclusions: FAPI PET/CT demonstrated heightened and extensive uptake in ILD compared to FDG, with the WL-SUVmean emerging as a potentially pivotal parameter for capturing metabolic information in ILD. Notably, the FAPI WL-SUVmean showed promise in PPF prediction. These findings underscore the potential utility of FAPI PET/CT as an imaging modality for diagnosing ILD.
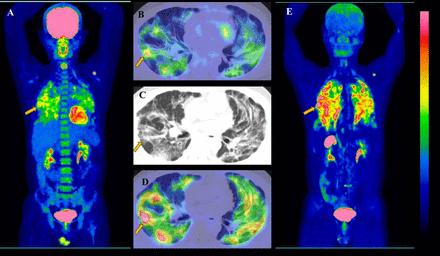
Figure 1, male, 46 years old, with IIP for 1month, manifests FDG and FAPI imaging positive. (A, E, the MIP of FDG and FAPI imaging; B-C, axial FDG PET/CT, CT and the FAPI PET/CT; The SUVmax of the foci indicated by the yellow arrow are 4.2 and 8.3 in FDG and FAPI PET/CT).