Abstract
24134
Introduction: Advances in molecular tumour profiling are driving the field of precision oncology. Programmed death-ligand-1 (PD-L1) is an immune inhibitory molecule aberrantly expressed in various aggressive human tumors, including breast cancer. Immune checkpoint inhibition therapy (ICI) uses monoclonal antibodies to inhibit PD-L1 mediated apoptosis of T-cells, but only a fraction of patients benefit from the promising treatment, emphasizing the need for non-invasive imaging for tumor characterization and patient selection. Highly selective anti-PD-L1-B11-IgG is commonly radiolabeled with 89Zr, but its recently developed derivative, B11-diabody-Fc, would benefit from radionuclide labeling with a shorter biological half-life, allowing for faster clearance from the blood pool and lower patient dose. As such, 44Sc is emerging as a potent PET radiometal due to its favorable decay properties (94% intensity, Eavg = 620 keV) and ‘goldilocks’ half-life of 4.04 hrs, suitable for small molecules, peptides, and antibody fragments. Herin, we report the first radiosynthesis and in vitro cell uptake assay of [44Sc]Sc-DTPA-anti-PD-L1-B11-diabody-Fc in PD-L1 positive and negative cell lines.
Methods: 44Sc was produced in-house via the 44Ca(p,n)44Sc reaction using a 12.8 MeV proton beam on a natCaO target, and passed through a two-column (DGA+SCX) purification system. Both anti-PD-L1-B11-IgG and -diabody-Fc were conjugated with p-SCN-Bn-DTPA, at 1:6 and 1:9 molar concentration, respectively, in PBS at pH 9 for 90 min at 37 °C. Unconjugated DTPA was removed via a PD-10 size exclusion column with 0.1M NaOAc buffer (pH 6) as eluent. Equal concentrations (5.55 MBq/25 µL) of 44Sc were added to each reaction vial and given 30 min at RT to complex. The radiochemical yield was determined via r-TLC using 0.2M Na citrate (pH 6) as the mobile phase. Where RCY was <95%, a second PD-10 size exclusion purification was performed. For the in vitro cell uptake study, murine breast cancer cells (E0771-PD-L1 + and E0771-PD-L1 knockout) were plated in a 6-well plate at a concentration of ~1x106 cells/well. After overnight culture, 2.2 pmol of [44Sc]Sc-DTPA-anti-PD-L1-B11-IgG and 54.4 pmol of [44Sc]Sc-DTPA-anti-PD-L1-B11-diabody-Fc were added to each well and incubated for 2h at 37°C. Post-incubation, the cells were washed with HBSS, trypsinized, and counted using a gamma counter with the uptake expressed as % dose per 1 x 106 cells.
Results: Radiochemical yield was >96% for the radiolabeled B11-diabody-Fc and >83% for B11-IgG (before PD-10 purification).
Table 1: Summary of apparent activity and radiochemical yield of [44Sc]Sc-DTPA-anti-PD-L1-B11-IgG and [44Sc]Sc-DTPA-anti-PD-L1-B11-diabody-Fc. *after PD-10 purification.
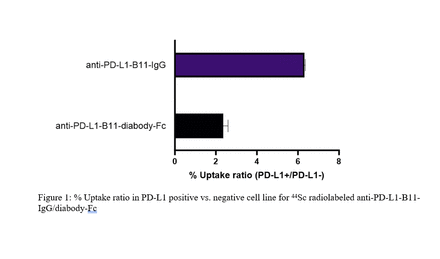
Both compounds showed significantly higher uptake in the PD-L1+ cells as compared to the knockout (p=5x106 for B11-IgG and p=7x106 for B11-diabody-Fc). The % uptake ratio in PD-L1+ cells vs. PD-L1- cells was ~three-fold higher in 44Sc radiolabeled B11-IgG than B11-diabody-Fc, due to higher specific binding affinity.
Conclusions: Successful synthesis and cell labeling of [44Sc]Sc-DTPA-anti-PD-L1-B11-diabody-Fc and its full length counterpart (B11-IgG) are reported with significant uptake in the PD-L1 + cell line. This foundational data demonstrates the potential utility of the diabody for quantifying PD-L1 expression, aiding in effective patient screening for ICI therapy.
Acknowledgement: We thank the Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of Radiology at Mayo Clinic, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of NIH grants UL1TR002494/UL1TR002377, and Minnesota Partnership for Biotechnology and Medical Genomics Translational Product Development Fund, awarded to MKP as PI, for funding this study.