Abstract
241178
Introduction: Myocardial perfusion (MP) SPECT is a well-established technique to diagnose coronary artery disease (CAD). Meanwhile, invasive coronary angiography (ICA) serves as the gold standard for diagnosing CAD, providing a clear visualization of coronary arterial stenosis and subsequent blood flow. In this study, we aim to extract radiomic features from non-invasive stress/rest MP SPECT to establish a binary ICA-based CAD prediction model.
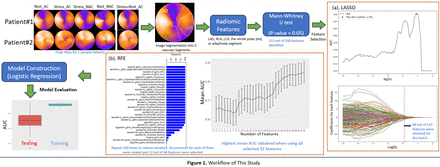
Methods: We retrospectively enrolled 220 patients who underwent standard one-day 99mTc-sestamibi SPECT/CT stress/rest protocol using a standard clinical NaI dual-head SPECT scanner. The projection data was reconstructed with CT-based attenuation correction (AC) or without AC (NAC). The reconstructed images were transformed into polar plots, which were segmented into three regions of interest (ROI), i.e., left anterior descending (LAD), right coronary artery (RCA), and left circumference (LCX). ICA was performed within 9 months following the MP SPECT scan, and a luminal diameter narrowing ≥70% in the LAD, RCA, or LCX was defined as obstructive CAD. The datasets were divided into 80% and 20% for training and testing cohorts. For training, 558 features were extracted using either LAD, RCA, LCX, the whole polar plot or adaptively choosing one of the vascular segments according to the known ICA diagnosis. For testing, LAD was input for feature extraction and prediction. We evaluated models established from AC and NAC data, as well as stress, rest, and combined stress and rest (stress+rest) data by averaging the stress and rest polar plots. The extracted features were normalized using the Z-score normalization. We first used the Mann-Whitney U test to identify features significantly correlated with the ICA diagnosis (p <0.05). Then Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression followed by Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) were employed for selecting relevant features. Selected radiomic features were used to construct predicting models using Logistic Regression (LR) with ten-fold cross-validation. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and accuracy (ACC) were used to assess the models’ predictive capacity.
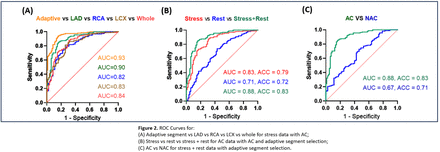
Results: For the stress data, extracting features using LAD, RCA, LCX, or the whole polar plot as ROI resulted in training AUC being 0.90, 0.82, 0.83, and 0.84 respectively, lower than using the adaptive ROI (AUC=0.93). By the Mann-Whitney U test, stress+rest with AC had the most significant features (224), followed by stress (215), and rest (190) among 558 features. The feature selection process using RFE and LASSO further reduced radiomic features to 32, 27, and 16 for the stress+rest, stress, and rest data. Stress+rest with AC feature set also showed the best prediction performance in the testing cohorts (AUC=0.88, ACC=0.83), followed by stress with AC (AUC=0.83, ACC=0.79) and rest with AC (AUC=0.71, ACC=0.72). AC feature sets significantly outperformed NAC for stress, rest, and stress+rest images (AUC=0.67, ACC=0.71), which was the highest among NAC data.
Conclusions: Our radiomics model built from stress/rest MPI SPECT exhibited a substantial predictive capacity for ICA-based CAD diagnoses. AC, adaptive feature selections, and combined stress and rest data further enhance the model performance.
Acknowledgment: This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund of Macau (0016/2023/RIB1).