Abstract
241038
Introduction: Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) have shown a five-fold increase in the past three decades and lutetium-177 (Lu-177) DOTATATE peptide radionuclide therapy (PRRT) has become the mainstay of treatment for locally advanced or metastasized NETs that overexpress somatostatin receptor subtype 2. The current dosing regimen involves 4 cycles of treatment with 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) every 8 weeks. A Ga-68 DOTATATE imaging routinely precedes PRRT to validate the presence and extent of the disease. The treatment is highly effective with favorable overall clinical outcomes, however, the dose to the radiosensitive organs such as the breast and thyroid in various patient populations has not been well-documented. Purpose: To determine the radiation absorbed dose to the female breast and thyroid following Lu-177 DOTATATE PRRT in order to assess the necessity for a more personalized therapy regimen. Our hypothesis was that patient demographics will play a significant role in the radiation absorbed dose to the female breast and thyroid following Lu-177 DOTATATE PRRT. This hypothesis was tested using voxel based dosimetry from Ga-68 DOTATATE biokinetics.
Methods: Five female patients from different age groups who underwent Ga-68 DOTATATE imaging, and who were diagnosed to be free of neuroendocrine tumors, were chosen for this retrospective study. Based on the administered Ga-68 DOTATATE activity, post-injection imaging time, an extrapolated effective whole-body half-time for 0.05 Gy/GBq from literature, and a total administered dose of 29.6 GBq (800 mCi) for the Lu-177 DOTATATE, we performed OLINDA/EXM voxel level dosimetry by drawing volume of interest (VOI) curves in both breasts and in the thyroid of each patient using the Hermes System. Dose volume histogram (DVH) curves were generated and the maximum absorbed dose to each of the organs were compared using graphs for patient age and body weight.
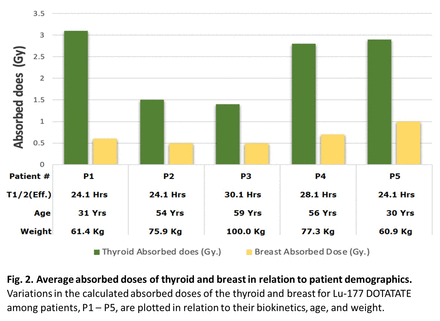
Results: Our DVH results, on average, revealed a maximum absorbed dose from Lu-177 DOTATATE to the thyroid of 5 Gy (range: 3-7 Gy) and to the breast of 1 Gy (range: 0.8 – 1.8 Gy) for all patients (Fig. 1). The average absorbed dose in the thyroid ranged from 1.4 - 3.1 Gy, and in the breast from 0.5 - 1 Gy (Fig. 2). The average effective half-life was 26.1 hrs. (range: 24.1 – 30.1 hrs.) and appeared to be more or less stable among all the patients. Patient 1, a 31-year-old with a history of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, displayed a higher average absorbed dose value for the thyroid at 3.1 Gy, while the breast dose was 0.6 Gy. This patient also had an elevated chromogranin level of 527 ng/ml. Patients 2 and 3, aged 54 and 59, respectively, exhibited the smallest average absorbed dose in the thyroid, ranging from 1.4 to 1.5 Gy. Additionally, they both had similar average absorbed doses of 0.5 Gy to the breast. Patient 4, with a benign pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, had an absorbed dose of 2.8 Gy for the thyroid and 0.7 Gy for the breast. And finally, patient 5, the youngest in this group at 30 yrs., had a malignant meningioma, specifically on the left optic nerve, had an average absorbed dose of 2.9 Gy for the thyroid and 1 Gy for the breast.
Conclusions: In general, thyroid absorbed doses were higher than breast doses in all individuals. Moreover, thyroid doses appeared to be higher in younger individuals than in older, whereas breast doses were more uniform among all patients. A larger study is warranted to explore the implications of age and thyroid dose gleaned from this study.