Abstract
24102
Introduction: 15O-gas PET is very useful for the diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases because it can quantitatively measure CBF, CBV, OEF, and CMRO2 in a single examination. At our hospital, we use the ARG method, in which C15O2, 15O2, and C15O gases are inhaled in sequence, and continuous arterial blood sampling and arterial blood radioactivity measurement are performed. Recently, high-sensitivity 3D-PET scanners optimized for whole-body FDG-PET examinations, have become popular. When such scanners are used for 15O-gas PET, deadtime and scatter correction may be challenging, especially if the detector is BGO. Reducing the inhaled activity, however, decrease the blood radioactivity and may enlarge the statistical noise in the measured input function. In this study, we evaluated the measurement accuracy of brain radioactivity when 15O-gas PET is performed on the currently available whole-body 3D-PET/CT scanner, and determined the optimal radioactivity concentration of 15O-gas. Furthermore, CBF thus-measured was compared with the perfusion measured with SPECT on the same subjects.
Methods: A 3D-PET/CT scanner, Discovery IQ, which has a 5-ring configuration of BGO detectors with 26cm axial FOV, was used.
Phantom Study:1.A cylindrical phantom was filled with 500MBq of 11C and a dynamic scan was performed to measure prompt, random and NEC. 2.A 100mL saline-bag filled with 11C of 500MBq was placed on Hoffman 3-D brain phantom (HBP) filled with 18F of 20MBq and a dynamic scan was performed. Quantitative capability of measured radioactivity in HBP was evaluated from the PET images. 3.HBP filled with 18F of 20MBq was attached with a gas mask and the 15O-gas flow was introduced into it. Delivery of 15O-gas was decreased step by step from 3000MBq/min by 500MBq/min, during which time dynamic scan was performed. Quantitative capability of radioactivity in HBP and count rate characteristic was evaluated from the PET data.
Clinical Study:CBFs of PET and SPECT were compared in 10 patients (7 males, 3 females, 34-75years) with cerebrovascular diseases. Based on the results of phantom studies, patients inhaled C15O2 at 800MBq/min and 15O2 at 1000MBq/min, and a dynamic PET scan was performed while the arterial blood radioactivity was measured continuously. Then C15O was inhaled, and a PET scan and manual blood samplings were performed. CBF, CBV, OEF, and CMRO2 were calculated pixel by pixel by the ARG method. The analysis was performed using P-mod with standard brain transformation and alignment, and CBF of the same 26 regions including the cerebellum, each on the left and right sides, were averaged and compared. SPECT was performed by the ARG method using a single point arterial blood sampling with 123I- N-isopropyl-p-iodoamphetamine (IMP).
Results: Phantom Study: 1.When the radioactivity in the FOV reached 500MBq, prompts reached a plateau, indicating saturation and counting loss. 2.Radioactivity in HBP measured from the PET images approached true value as the radioactivity of 11C in the saline bag decreased. If 5% error is acceptable, radioactivity of 11C must be less than 30MBq. This corresponds to 1.8GBq/min with 15O-gas.[Fig.1] 3. To achieve quantitative accuracy of 5%, 15O-gas should be delivered at less than 1.0GBq/min. If it is above 1.5GBq/min, %Random exceeded 50%, which raises concerns about quantitative accuracy.
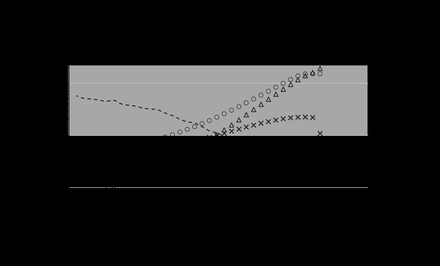
Clinical study: The correlation coefficient between PET and SPECT CBFs was 0.2. When three cases with large errors were excluded as outliers, it improved to 0.70, which showed a strong positive correlation. CBF of PET tended to be higher than that of SPECT.[Fig.2] The mean values of CBF, CBV, OEF and CMRO2 for all region were 32.8±10.3ml/min/100g, 3.1±1.2ml/100g, 0.56±0.10, and 3.3±1.3ml/min/100g.
Conclusions: 15O-gas PET using a high-sensitivity whole-body 3D-PET/CT scanner can be performed by adjusting the radioactivity concentration to 800-1000MBq/min. PET was able to measure CBF more quantitatively than SPECT and was able to measure CBV, OEF, and CMRO2.