Abstract
P984
Introduction: The differentiation of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) from oncocytoma is challenging with the current imaging techniques. By result, resection has traditionally been the treatment of choice for patients presenting with solid renal masses concerning for malignancy. Recently, 99m Tc-sestamibi SPECT/CT imaging has been employed in the work-up of solid renal masses with the hope of reducing unnecessary procedures. The ideal target to background ratio used to differentiate oncocytomas from renal cell carcinomas remains unknown. We report our institutional quantitative analysis of 99m Sestamibi SPECT/CT Imaging in conjunction with disease confirmation through tissue diagnosis.
Methods: 99m Tc-sestamibi SPECT/CT scans were performed on patients with one or more renal masses detected on prior CT or MR imaging. Using MIM software (a nuclear medicine image display, processing, and fusion software), the counts in the area of the masses were compared to the background counts in the normal area of the kidney using manually generated regions of interest. The target to kidney background ratio (TBR) of the renal mass was calculated. Of the 75 patients imaged, 52 patients had histologic diagnosis via either percutaneous biopsy or surgical resection. Histology was not available for the remaining 23 patients at the time of this study. In total, histology was available for 56 masses as several patients had multiple masses. The TBRs of these masses were then compared to the histologic diagnoses.
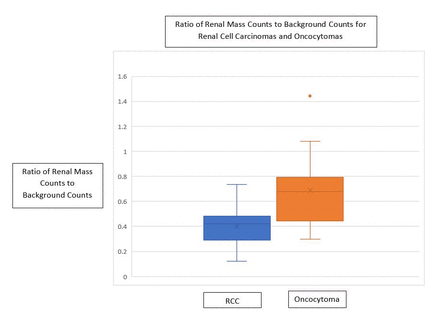
Results: Of the 56 masses sampled or resected, 35 were diagnosed as RCC and 14 were diagnosed as oncocytomas. The remaining masses were diagnosed as other benign tumors (N=2) or metastatic disease from a non-renal primary (N=1). The average target to background ratio for the RCC’s was 0.40 (90%CI, 0.36-0.44), (Range: 0.12-0.73) and the average target to background ratio for the oncocytomas was 0.72 (90%CI, 0.58-0.86), (Range: 0.30-1.44).
Conclusions: The quantitative analysis of renal masses evaluated with 99m Sestamibi SPECT/CT Imaging revealed a difference in the radiotracer uptake of oncocytoma and renal cell carcinoma. Further research is needed to validate the results and determine the utility of 99m Sestamibi SPECT/CT Imaging in clinical practice.