Abstract
P673
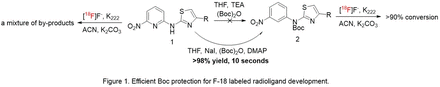
Introduction: Pyridine derivatives are one of the most commonly studied heterocycles for incorporation of [ 18F]fluoride and thus the resultant ortho-[18F]fluoropyridines have emerged as a widely used functionality in PET tracers. 1-(Pyridin-2-yl)thioureas are versatile building blocks for synthesizing N-(pyridin-2-yl)thiazol-2-amine derivatives, which are used to construct a variety of heterocycles and bioactive compounds. Direct 18F substitution by using NO2 as a leaving group at ortho and para positions is atom efficient, however, very few (Pyridin-2-yl)thiourea derivatives bearing a nitro functionality have been reported so far. This is due to the highly reactive nature of the nitro group and the unreactive nature of the amino group on the electron deficient pyridine ring. While the unreactive amino group may still react with the highly reactive nitro group at high temperature (80 degree), leading to a complex of by-products during radiolabeling. Therefore, protection of the free unreactive amino is of great significance, however, we found the protection of unreactive amino did not proceed at all using Boc anhydride with triethylamine as a base. Here we report the novel and efficient Boc protection method via solvent gelation process.
Methods: Boc protection of 1 was performed in THF. Compound 1 with 1.0 equivalent of NaI were dissolved in THF, followed by addition of 2.0 equivalents of (DMAP) and 5.0 equivalents of Boc anhydride. The reaction was carried out at room temperature, and after 10 seconds the whole reaction mixture formed a gel, in which compound 2 was detected in >98% yield.
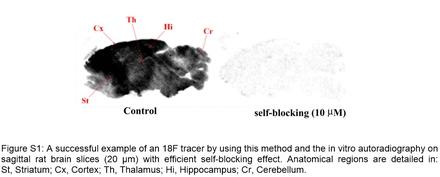
Results: By using the combination of NaI-DMAP-Boc in Boc protection, compound 1 could be efficiently protected by Boc anhydride. Boc protected product 2 could be achieved in >98% yield at room temperature within a few seconds. The radiolabeling of 2 led to >90% conversion without clear by-products. Subsequent deprotection could be conducted by addition of an acid (TFA) to the reaction mixture to afford the desired probe.
Conclusions: Boc protection of 1 using the traditional method did not give any product 2. This is due to the unreactive nature of the amine caused by the highly electron deficient pyridine ring worsened by the strong electron withdrawing effect of nitro group. Compound 2 could be prepared from compound 1 in >98% yield within 10 seconds by using the modified protection procedure. Direct reaction of 1 with 18F led to a mixture of unidentified by-products, while reaction of 2 with 18F gave >90% conversion of 18F without clear by-products. As a useful general method, we believe the efficient protection will enable research and application for a variety of 18F PET ligands. Acknowledgements: These studies were supported by NIH/NIA grant K25AG061282.