Abstract
P44
Introduction: The aim of our work is to compare predictive, pre-therapy Tc-99m macroaggregated albumin (MAA) SPECT/CT based dosimetry vs. post-therapy Y-90 PET/CT derived dosimetry in patients undergoing locoregional therapy to the liver with Y-90 microspheres.
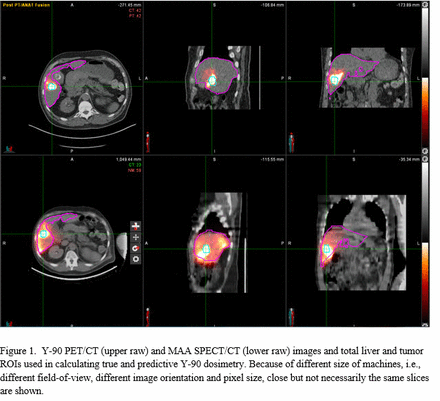
Methods: After treatment with Y-90 microspheres 16 patients (3 female:13 male, mean age 68.2±5.3y), underwent PET/CT imaging. Images were acquired for 15 min. The low dose, non-diagnostic CT images from PET/CT were used for localization of the Y-90 microspheres and attenuation correction. The reconstruction matrix size was 200x200x75 mm and voxel size 4.07x4.07x3.00 mm. Two weeks prior to Y-90 therapy the patients also had MAA SPECT/CT performed on a dual-head Infinia SPECT/CT gamma camera (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI), with LEHR collimator and activity of 185 MBq was used. For the SPECT/CT studies, 60 views at 30 s per view were acquired and images were reconstructed using an ordered subset expectation maximization (OSEM) algorithm. Attenuation correction was performed using the CT scan, the reconstruc­tion matrix size was 128 × 128 and the pixel size was 4.4 mm. The CT was performed with 10mm axial sampling, 140 kVp, 2.5 mA, 2.6 rpm and with 256 × 256 matrix size. The data were reconstructed using the vendor's reconstruction software and were transferred to a common platform where the SPECT/CT and PET/CT images (Fig.1) were used to calculate Y-90 dosimetry using MIM 7.1software (MIM Software Inc., Cleveland, Ohio). Local deposition method with known activity of Y-90 was used to calculate dosimetry.
Results: For 16 patients, the mean liver, tumor (T) and normal tissue (NT) doses (mean ± SD) for MAA SPECT/CT studies were, 42.02±22.36 Gy, 234.72±172.54 Gy and 41.22 ±20.37Gy, respectively. For Y-90 PET/CT studies the same values were 49.85±24.88 Gy, 314.07±197.02 Gy and 46.18 ±20.52Gy, respectively. The average differences between the liver, T and NT MAA and Y-90 doses were 18%, 25% and 15%, respectively and the linear correlation between the respective doses were r= 0.86, r= 0.71 r= 0.95, respectively.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that, post-therapy Y-90 PET/CT dosimetry average values have tendency to be slightly higher in comparison with MAA SPECT/CT dosimetry values. Also, if the catheter tip positions in MAA and Y-90 studies are positioned very similar and far from major bifurcations, the main source of differences between MAA and Y-90 dosimetry values are attributed to differences in respective ROI's. This is especially case for small, less than 10cm3, tumors, where the differences can be large. The best correlation between MAA and Y-90 dosimetry was achieved for NT, providing very good estimates for not exceeding 40 Gy guideline limit for NT in Y-90 therapies.