Abstract
P378
Introduction: To evaluate two experimental imaging radiopharmaceuticals as diagnostic partners for a theranostic approach to alpha-particle therapy in patients suffering from metastatic melanoma. These radiopharmaceuticals target the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R). The primary objectives were safety and tracer biodistribution. Secondary objectives included the suitability of [68Ga]VMT02 PET/CT imaging for patient selection prior to future studies of [212Pb]VMT01 radiopharmaceutical therapy, and [203Pb]VMT01 SPECT/CT imaging for predictive dosimetry of [212Pb]VMT01 radiopharmaceutical therapy.
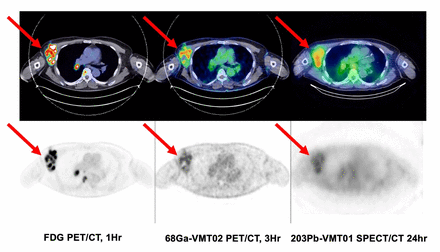
Methods: This was a prospective IRB-approved phase 1 first-in-human trial evaluating the safety and biodistribution of [203Pb]VMT01 for SPECT/CT imaging and [68Ga]VMT02 for PET/CT imaging. The study design included a randomized cross-over of [203Pb]VMT01 SPECT/CT Imaging followed by [68Ga]VMT02 PET/CT Imaging (or vice versa) of patients with stage IV metastatic melanoma. 15 to 25 mCi (555 to 925 mBq) of [203Pb]VMT01 was injected IV with imaging performed at 1 hour, 4 hours and 24 hours, including whole body planar imaging on a GE 670 scanner, and whole body SPECT/CT imaging on a Spectrum Dynamics Veriton 64 scanner. 2.0 to 7.5 mCi (74 to 277 mBq) [68Ga]VMT02 was injected IV and imaging was performed on a Siemens Vision 600 PET/CT dynamically up to 1 hour, then at 2 hours and 3 hours. Patient selection included a positive [18F]FDG PET/CT performed within 30 days of experimental radiopharmaceutical injection. Key FDG-avid melanoma lesions were marked on a [18F]FDG PET/CT, and presented to three experienced Radiologists serving as blinded reviewers. The blinded reviewers compared the [18F]FDG PET/CT to the experimental imaging performed at different time points and scored the scans and key lesions on multiple metrics. Organ and tumor dosimetry calculations were performed. Since [203Pb]VMT01 is a chemically identical surrogate for [212Pb]VMT01 therapy, [203Pb]VMT01 SPECT/CT imaging was used for dosimetry calculations of future alpha-emitting therapy. The trial was overseen by an independent safety review committee (SRC). Safety monitoring included physical exams, laboratory assessments, and ECGs before, during and after therapy with follow-up for 30 days after the last injected experimental radiopharmaceutical. Blood and urine samples were obtained at multiple timepoints for analysis.
Results: Six patients were imaged prospectively. No safety issues related to either experimental imaging radiopharmaceutical were identified by the SRC. Blinded reviewers found that 50% of the patients had tumors positive on [68Ga]VMT02 PET/CT imaging (above background liver activity), suggesting they would have been selected as eligible for future [212Pb]VMT01 therapy. [68Ga]VMT02 PET/CT imaging at the 3-hour time point resulted in the best tumor to background conspicuity of the metabolically active melanoma metastases. Dosimetry calculated for [68Ga]VMT01 has lower systemic and organ radiation exposure than [18F]FDG. [203Pb]VMT01 SPECT/CT imaging showed retention of radiopharmaceutical within tumors at 24 hours post injection. Dosimetry for [203Pb]VMT01 showed acceptable radiation exposure.
Conclusions: No safety concerns were identified for IV injection of [203Pb]VMT01 or [68Ga]VMT02 into humans. [68Ga]VMT02 PET/CT may be useful for identifying MC1R expression on tumors in patients with metastatic melanoma, allowing for selection for [212]VMT01 alpha-emitting radiopharmaceutical therapy in future studies. [203Pb]VMT01 allowed for calculations of organ and tumor dosimetry for future [212Pb]VMT01 therapy.