Abstract
P238
Introduction: In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), fibroblast-like synoviocyte cells, which are involved in inflammation of the articular cartilage and bone, overexpress fibroblast activation protein; a feature that could be leveraged to improve imaging assessment of disease. The Purpose of the study is to determine the performance of 68Ga-FAPI in assessing joint disease activity of RA and to compare with 18F-FDG imaging.
Methods: Twenty RA patients (15 women; mean age, 55±10 years) with moderate to high disease activity according to Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) were prospectively enrolled and underwent clinical and laboratory assessment of disease activity and dual-tracer PET/CT (68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG) imaging. The clinical disease activity assessment included physical examination of the joints (tender joint count [TJC] and swollen joint count [SJC], using 28-joint counts), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), patient assessment of pain, patient global assessment (PGA), and evaluator global assessment (EGA) of disease activity, patient self-report questionnaire of physical function assessment (Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index [HAQ-DI] and the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36 [SF-36]). The composite indices for disease activity included CDAI, Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI), and Disease Activity Score using 28-joint counts (DAS28) with ESR or CRP. Imaging derived variables of PET joint count (PJC, number of PET positive joints) and PET Articular Index (PAI, a sum of the points of the joints using a 3-point scale) were analyzed for correlation to clinical and laboratory variables of disease activity.
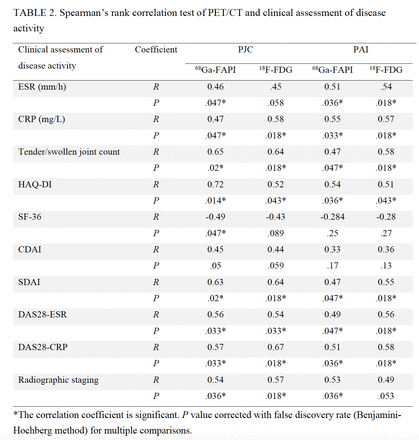
Results: The combined output of both PET/CT techniques detected 244 affected joints; all of which were positive by , while 15/244 (6.1%) FAPI-avid joints in 6/20 (30.0%) participants were not detected by . The SUVMAX of the most affected joint in each participant was significantly higher in 68Ga-FAPI than in 18F-FDG PET/CT (9.54±4.92 vs. 5.85±2.81, P = .0006) (Figure 1). The SUVMAX of the joints by both 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT were positively correlated with CRP levels (r = 0.49, P = .03 and r = 0.54, P = .01, respectively). In clinical assessment, 237 tender or swollen joints were determined by physical examination. When combining physical examination and PET/CT, a total of 314 joints were found to be involved. Among them, 167 joints were positive in both physical examination and 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. The positive rate of detecting involved joints was 75.5% (237/314) for physical examination and 77.7% (244/314) for 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. The matching rate of physical examination and 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT was 53.2% (167/314). The PJC and PAI scores by 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT were positively correlated with the tender or swollen joint counts (r = 0.65, P = .02 and r = 0.47, P = .047, respectively), ESR (r = 0.46, P = .047 and r = 0.51, P = .036, respectively), CRP (r = 0.47, P = .047 and r = 0.55, P = .033, respectively), HAQ-DI (r = 0.72, P = .014 and r = 0.54, P = .036, respectively), SDAI (r = 0.63, P = .02 and r = 0.47, P = .047, respectively), DAS28-ESR (r = 0.56, P = .033 and r = 0.49, P = .047, respectively), DAS28-CRP (r = 0.57, P = .033 and r = 0.51, P = .036, respectively), and radiographic staging (r = 0.54, P = .036 and r = 0.53, P = .036, respectively). By 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT, the PJC was negatively correlated with SF-36 score (r= -0.49, P = .047) (Table 1).
Conclusions: In participants with RA who underwent 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT, the extent of joint involvement correlated with clinical and laboratory variables of disease activity and showed a greater amount and degree of affected joints than 18F-FDG PET/CT.