Abstract
P1536
Introduction: Radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis (RIPF) is a commonly observed late effect of radiation therapy on the chest. RIPF insidious onset and non-specific symptoms, which overlap with those of more common pulmonary and non-pulmonary diseases or age, lead to significant diagnostic delays. Because of the pivotal role of fibroblasts in pathogenic fibrinogenesis, fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP) overexpressed on activated fibroblasts is a promising biomarker for early disease detection. Consequently, we evaluated two FAP radiotracers to visualize in vivo FAP expression in a mouse model of RIPF by PET/CT.
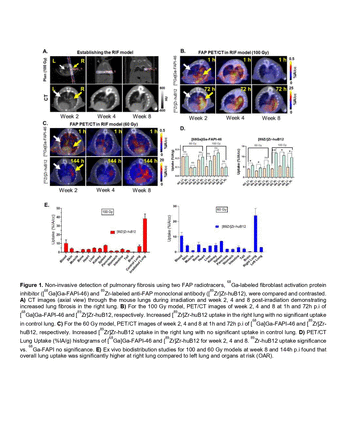
Methods: To induce fibrosis, a single X-ray fraction of 100 or 60 Gy was delivered to the right lung of male and female C3H/Hej mice in a Small Animal Radiation Research Platform (SARRP) using two 5 mm pencil beams (PA/AP), while avoiding the heart and spine. The contralateral lung was used as untreated control. Beginning at 2 weeks post-irradiation, animals received a clinical score assessing their overall health. Two FAP radiotracers, 68Ga-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor ([68Ga]Ga-FAPI-46) and 89Zr-labeled anti-FAP monoclonal antibody ([89Zr]Zr-huB12), were compared and contrasted. At 2-, 4-, and 8-weeks post-irradiation, mice were administered [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-46 into the lateral tail vein, and sequential PET/CT scans were acquired in an Inveon micro-PET/CT at 1-hour post-injection (p.i.). The following day, mice were intravenously injected with [89Zr]Zr-huB12 and scanned at 24, 72, and 144 hours post-injection. After the final imaging time point of 144 h, ex vivo biodistribution was performed, and lung tissues were collected for histology (Manson trichrome and FAP IHC). Volume of interest analysis of the PET/CT images was performed to determine whole-lung CT densities (HU) and radiotracer uptake as percent injected activity (%IA). Ex vivo tissue uptake was quantified as percent injected activity per gram of tissue (%IA/g) or percent injected activity (%IA) for the lung.
Results: In a bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-46 detected the early onset of pulmonary fibrosis. However, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-46 PET/CT showed poor uptake and retention in the irradiated lung at 1 hour post-injection. In mice receiving 100 Gy, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-46 uptake 1 h p.i. was 0.11 ± 0.02 %IA/cc (LL) vs. 0.17 ± 0.04 %IA/cc (RL) (p=0.12, ns); 0.23 ± 0.04 %IA/cc (LL) vs. 0.26 ± 0.03 %IA/cc (RL) (p=0.43, ns) and 0.09 ± 0.01 %IA/cc (LL) vs. 0.10 ± 0.01 %IA/cc (RL) (p=0.3, ns) for week 2, 4 and 8, respectively. Conversely, [89Zr]Zr-huB12 PET/CT scans at 24, 72, and 144 h p.i. displayed significantly elevated uptake in the irradiated lung. [89Zr]Zr-huB12 peak lung uptake, 72 hours p.i. was 4.1 ± 0.3 %IA/cc (LL) vs. 12 ± 2 %IA/cc (RL) (p=0.003); 5.5 ± 0.3 %IA/cc (LL) vs. 11 ± 1 %IA/cc (RL) (p=0.04) and 5.1 ± 0.6 %IA/cc (LL) vs. 10 ± 3 %IA/cc (RL) (p=0.02) for week 2, 4 and 8, respectively. Overall, lower [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-46 and [89Zr]Zr-huB12 uptake was observed in mice receiving 60 Gy, but with similar statistical trends. PET/CT imaging data aligned with the results of the ex-vivo analysis biodistribution. Histology analyses corroborated in situ fibrosis and FAP expression in radiate lungs.
Conclusions: Our results indicated the feasibility of [89Zr]Zr-huB12 PET/CT to detect FAP expression related to pulmonary fibrosis activity and progression in a murine model of RIPF. Additional studies will establish the sensitivity and specificity of [89Zr]Zr-huB12 PET/CT in RIPF and other translationally relevant models of fibrosis.