Abstract
P1298
Introduction: AdaptiSPECT-C is a dedicated brain imager designed to support drug discovery using Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT). The cameras for this system are designed around modular aperture plates that implement adjustable pinholes using a stationary segment and multiple moving segments. The stationary plate has the entrance cones for five pinholes capable of creating multiple projections on a single detector. The moving segments consist of five independently controlled shutters that each allow four distinct pinhole settings: high sensitivity, standard resolution, high resolution and closed (Figure 1). The fixed aperture plate is fabricated using a machinable tungsten base with printed tungsten inserts, while the moving adaptive aperture shutters are fabricated with printed tungsten due to their complex shapes. Each pinhole has a keel edge profile and the acceptance cone is appropriate for a volume sufficient for the human head. The chosen multi-pinhole collimator design offers many opportunities for optimizing image acquisition at different points during an uptake/washout pharmacokinetic study. The system can be adjusted to achieve different resolutions, sensitivities, and degrees of multiplexing.
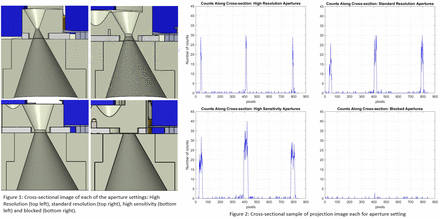
Methods: The adjustable multi-pinhole collimator was tested by using it to image a pertechnetate point source using a high-resolution gamma-ray detector known as iQID. A point source was suspended 20 cm in front of the adaptive collimator, which was in turn placed 3 cm in front of the iQID camera. Projection images of the point source were collected for each pinhole setting: high sensitivity, standard resolution, high resolution and blocked. The data from each set of shadow images were used to assess pinhole edge penetration and to determine whether any leakage was present in the aperture plate system.
Results: Results from the shadow casting shows insignificant leakage from the pinholes, implying that the keel edge design was sufficient for 140 keV photons. The aperture plate itself did not appear to have any leakage as seen in the cross-sectional samples (Figure 2) of averaged image acquisitions, which show distinctive images of the point source with only background counts away from the open pinhole areas.
Conclusions: The point-source projection data showed that the aperture mechanism permits flexible adjustment of pinhole dimensions and number of open pinholes, and sufficiently blocks unwanted 140 keV gamma rays at each aperture setting. To further improve upon the analysis of the collected data, we implement calibration measurements of the iQID camera into our quantitative methods. We also report on full point-spread function measurements by acquiring data from the point source translated throughout the three-dimensional field of view.