Abstract
P1064
Introduction: Clinical adoption of dynamic PET imaging for the quantification of myocardial blood flow (MBF) is increasing rapidly. However, effects from cardiac motion and periodic respiratory motion can significantly compromise perfusion image quality, ultimately impacting MBF accuracy and diagnostic ability. A prototype data-driven motion correction (DDMC) algorithm specifically for cardiac PET has been developed to correct for these effects. Studies have demonstrated substantial improvements to image quality of both patient scans and phantoms through use of DDMC and even the potential to restore images considered non-diagnostic due to significant motion blurring. Currently, there is limited understanding on the quantitative impact DDMC has on MBF estimation, especially amongst a broader population of clinical patients. This study evaluated the DDMC algorithm through comparing key image quality and perfusion parameters of test-retest cardiac PET scans.
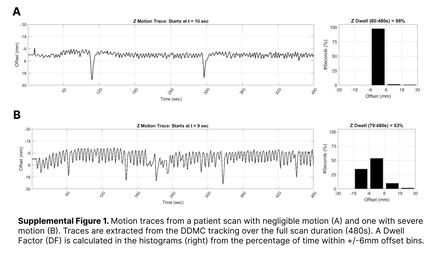
Methods: N=53 rest and repeat-rest (‘restQA’) 82Rb PET studies were identified in patients referred for the evaluation of CAD. These restQA scans are typically acquired using a reduced tracer dose (20-50% of the clinical dose) immediately after the standard rest scan, and before the vasodilator stress scan. List-mode scans were acquired on a Biograph Vision PET-CT scanner following standard clinical protocol. Dynamic images were then reconstructed with and without DDMC applied, resulting in 212 total images (N=106 pre-MC, N=106 post-MC). Motion was quantified using Dwell Fraction (DF), the percentage of time the heart motion vector is within a set range (6mm) from the corrected position. Image quality was assessed through image CNR, SNR, TBV, R2, Χ2 values. FlowQuant software was used for MBF quantification, resulting in dynamic time-activity curves (Bq/cc) and flow parameters for intercomparison using Bland-Altman analysis and paired t-tests.
Results: Average patient age was 62±15 years, and weight was 107±44 kg. 77% of patient scans had DF>0.9 suggesting minimal to no motion, 16% with 0.9>DF>0.7, and 7% displaying severe motion (DF<0.7). All image quality statistics on average showed stable or improvement post-MC (pre-MC vs. post-MC): CNR (rest: 6.61 vs 6.76, restQA: 6.46 vs 6.58; both p<0.05), SNR (11.27 vs 11.29, 11.22 vs 11.18; both p>0.05), R2 (0.978 vs 0.979, 0.974 vs 0.974), Χ2 (0.973 vs 0.965, 0.972 vs 0.969; both p>0.05). Notably, all scans with severe motion (DF<0.7) had increased CNR post-MC. The patient (DF=0.19) with the greatest motion also demonstrated marked improvement in goodness-of-fit metric (R2) from 0.89 to 0.97 post-MC. Slight differences were noted between pre- and post-MC areas under the arterial blood time-activity curves (rest: 24.1 vs 23.5 MBq/cc∙s, restQA: 11.1 vs 10.8; both p<0.05); whereas myocardial tissue TAC was the same (38.1 vs 38.3, 17.0 vs 17.1; both p>0.05). Average MBF values were consistently increased following DDMC (rest: 1.02 vs 1.05, restQA: 1.0 vs 1.03; both p<0.05). In addition, visual analysis of flow polar maps of scans with severe motion showed heterogenous and severely underestimated values that were corrected following motion correction. Bland-Altman analysis of rest-retest MBF values showed consistent differences of <20% in mean flow and 5-segment flow in both pre- and post-MC. Overall, 50 out of the 53 (94%) patients had less than a 10% change and 79% with less than a 5% change in rest-retest MBF values following DDMC.
Conclusions: Data-driven motion correction of cardiac 82Rb PET scans produced image reconstructions of at least equal or improved image quality, and stable MBF quantification as compared to images without motion correction. Significant improvement to image quality and consistency of MBF estimation was seen in scans with severe cardiac/respiratory motion, with some cases being completely rescued following DDMC. This DDMC approach appears to offer quantitative and qualitative benefit for scans with significant motion and does not degrade or harm reconstructions without motion, suggesting the potential for routine clinical application.