Abstract
P105
Introduction: Acute myocardial infarction usually results in the ischemic death of cardiomyocytes, leading to myocardial inflammation and remodeling processes due to upregulation of chemokine synthesis and subsequent inflammatory cell infiltration. Especially the synthesis of chemokine CXCL-12 in the damaged myocardium leads to the recruitment of C-X-C-motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) positive immune cells. CXCR4 is expressed on cell surface of various immune cells and plays an important role in stem cell mobilization, orchestration of inflammatory response and wound-healing. It is known that the accumulation of CXCR4 positive immune cells after myocardial infarction can be detected non-invasively using radiolabeled receptor ligands. Until now, in vivo visualization of CXCR4 expression was mostly performed using the positron emission tomography (PET) tracer Ga-68-Pentixafor. However, use of PET/CT is often limited to specialized centers. For a broad application in worldwide clinical practice, there is a need of CXCR4-directed ligands labeled with isotopes that can be used with conventional scintigraphy or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) like technetium-99m. This is the first report of non-invasive detection of CXCR4 expression after acute myocardial infarction in human by SPECT/CT using Tc-99m-N4-CXCR4.
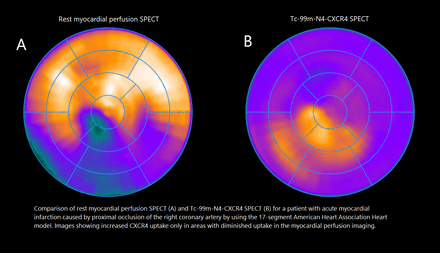
Methods: Nine patients (8 men and 1 women, mean age 62 ± 21 years) with acute myocardial infarction underwent imaging with Tc-99m-N4-CXCR4-SPECT/CT within 3 to 4 days after symptom onset and imaging with rest myocardial perfusion SPECT within 2 to 6 days after symptom onset. All patients had undergone mechanical revascularization within 10 hours after symptom onset and received standard of care medical treatment. Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy was performed using a CZT-based gamma camera (D-SPECT Cardio, Spectrum Dynamics Medical) and scintigrams were interpreted using the current EANM procedural guidelines for clinical routine. The CXCR4-directed scans were acquired one hour post-injection using a SPECT/CT system (Siemens Symbia T, Siemens Healthineers). First, images were inspected visually. For quantification of increased CXCR4 expression in the myocardium a score classifying no, mild, moderate and intense uptake was utilized. Areas with increased CXCR4 expression were compared to the myocardial perfusion scans by using the 17-segment American Heart Association Heart model for both scans. For semi quantitative analysis, a 1 cm3 volume of interest (VOI) was placed over the infarcted area to derive maximum und medium uptake values. For reference, blood pool (descending aorta), spleen and bone marrow (using average uptake of T9, T10 and T11) was assessed. Signal-to-background ratios were calculated.
Results: CXCR4-directed-SPECT was visually positive in all nine patients, with three patients showing moderately and six patients showing mildly increased tracer uptake. Comparison of CXCR4-targeted and myocardial perfusion SPECT demonstrated increased CXCR4 expression only in areas with diminished uptake in the rest myocardial perfusion imaging corresponding to the affected vessel in coronary angiography in all patients. The maximum uptake value ratio of lesion to blood pool was 2.36. Uptake in bone marrow and spleen were elevated above blood level and showed good correlation with uptake in the infarcted areas (r=0,79 for spleen and r=0,77 for bone marrow).
Conclusions: This is, to our knowledge, the first report of in vivo imaging of CXCR4 after acute myocardial infarction using a Tc-99m-labelled tracer. Increased CXCR4 expression in the infarcted region was observed in all nine patients showing a good signal to background ratio as compared to blood pool. This first proof-of-concept investigation demonstrates the general feasibility to evaluate CXCR4 expression after acute myocardial infarction using conventional scintigraphy or SPECT techniques and might thus broaden its worldwide application in clinical practice.