Abstract
4059
Introduction: Prostate cancer (PC) is the most common cancer in men in the world. In America about 1 man in 8 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime. The average age of men at diagnosis is about 66 yo. Hormone therapy for prostate cancer can block the production or use of androgens. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonists, prevent the pituitary gland from secreting luteinizing hormone (LH). LH acts on specific cells in the testes to produce the majority of testosterone in the body. In this way LHRH decreases the amount of testosterone secreted by the testes. It is important to decrease testosterone level because once it binds to androgen receptors in PC cells stimulating the expression of specific genes that cause PC to grow. Also it must be noted that receptors for LH-RH are found on most PC cells and these receptors persisted despite prolonged exposure to LH-RH agonists.
Up to 70% of PC are androgen-dependent at the time of diagnostic, and therefore treated with androgenic therapy. At the moment, there are no 99mTc-based radiotracers that target LHRH for PC diagnosis and treatment monitoring. Our aim was to develop and evaluate a 99mTc radiolabeled HYNIC-GSG-(DLys6)-LHRH analogue as a novel PC imaging agent.
Methods: Twenty micrograms of HYNIC-GSG-(DLys6)-LHRH (GeneScript, EEUU) was radiolabeled with 99mTc at 50°C for 20 min, in presence of four different co-ligands (Tricine, Tricine/Nicotinic Acid (AN); ethylenediaminediacetic acid (EDDA) and Tricine/EDDA). Final formulation conditions were optimized and analyzed by ITLC-SG and by HPLC to achieve the highest radiochemical purity (≥98%). Log D and in vitro stability in both serum and L-Cysteine were evaluated up to 4 h at 37°C. In vitro cell binding studies were analyzed in different human prostate cancer cell lines (LnCap, PC3, Du-145) and a normal human prostate cell line (RWPE-1), up to 60 min at 37°C (50 nM). Biodistribution studies were performed in Swiss normal mice and in LnCap tumor-bearing nude mice (n = 4 per time), at 3 and 6 h post-injection. Organs and tissues were measured using a High Purity Germanium (HPGe) detector (Canberra). 99mTc-HYNIC-GSG-(DLys6)-LHRH/Tricine/AN SPECT-CT (Mediso) images were acquired at 1, 3 and 6 h post-injection.
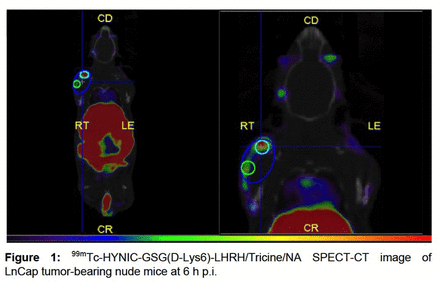
Results: 99mTc-HYNIC-GSG-(DLys6)-LHRH/Tricine/AN complex showed a radiochemical purity of 99.83 ± 0.29 % by HPLC and 99.50 ± 0.17 % by ITLC-SG, with a Log D= -2.82 ± 0.04 being stable in different in vitro analyzed conditions. Binding affinity and specificity of 99mTc-HYNIC-GSG-(DLys6)-LHRH/Tricine/AN in different PC cell lines (LnCap, PC3, Du-145) showed relevant membrane-bound results in all of them, with little internalization. We did not observe significant binding affinity in RWPE-1 cell line with this tracer. Biodistribution and SPECT/CT imaging in normal Swiss mice and LnCap tumor-bearing nude mice revealed high kidney, liver, gastrointestinal uptake and also relevant tumor uptake (tumor-to-muscle ratios of 9.96 and 4.42 at 3 and 6 h, respectively) (Figure1).
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the use of the 99mTc-HYNIC-GSG(D-Lys6)-LHRH/Tricin/NA represents a novel molecular imaging agent for diagnosis and monitoring of LHRH receptor-expressing PC, which would lead to selective targeting.