Abstract
4011
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is known as a common malignant neoplasm worldwide. Tumor hypoxia is a common feature in CRC and involves radiotherapy and chemotherapy resistance. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop specific targeting probes for hypoxic CRC therapy to improve survival rate and quality of life. Carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9) protein is abundantly expressed in hypoxic CRC and is considered a specific marker for targeted therapy. This study developed a nuclear medicine therapeutic agent probe, which CA9 targeting peptide (CA9tp) coupled with CA9 inhibitor acetazolamide (AAZ) and labeled radionuclides to treat hypoxic CRC xenograft models.
Methods: We use an automatic microwave peptide synthesizer to produce dual CA9 targeting probes (AAZ-CA9tp), which are bonded to 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid ( DOTA) and labeled with Lu-177 (177Lu-DOTA-AAZ-CA9tp) for providing cell binding and toxicity assay in vitro, and imaging, treatment, and biodistribution analysis in vivo.
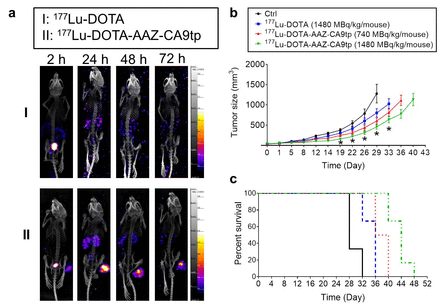
Results: The 177Lu-DOTA-AAZ-CA9tp was showed high serum stability, high cell surface binding affinity, and toxicity in vitro. We further indicated that the 177Lu-DOTA-AAZ-CA9tp remarkably increased in hypoxic tumor tissues of HCT15-bearing xenograft mice compared to control groups. 177Lu-DOTA-AAZ-CA9tp can inhibit tumor proliferation, prolong the survival rate in HCT15 xenograft.
Conclusions: Our results showed that the isotope-labeled imaging agent (177Lu-DOTA-AAZ-CA9tp) might be a potential tool for hypoxic CRC diagnosis and therapy in clinical.