Abstract
3372
Introduction: AIM: To evaluate the prognostic value of gated 99mTc-MIBI SPECT (GSPECT), gated 18F-FDG PET (GPET) and left ventricular wall thickness (LVWT) by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM).
Methods: MATERIALS AND METHODS: Seventy-five consecutive patients (mean age, 57±10 y, 69 men) were retrospectively recruited from a study population referred to the Anzhen Hospital of Capital Medical University from January 2017 to August 2020 for myocardial viability assessment. All the patients underwent GSPECT, GPET and CMR within two weeks, with a mean follow-up of 31 months (range, 0.3-55.5months). Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF, %) measured by GPET, GSPECT and CMR, respectively. End diastolic volume (EDV, mL) and end-systolic volume (ESV, mL) measured by GPET, GSPECT and CMR and corrected for BSA and EDVI and ESVI were calculated. Hibernation myocardium (HM) by PET and end-diastolic wall thickness (EDWT, mm) by CMR were analyzed using a 17-segment model. A total of 547 segments with EDWT<6mm, which was considered as reduced LVWT, were divided into three groups by with or without HM, defined as perfusion-metabolism mismatch. Group 1 (Normal perfusion), Group 2 (HM+) and Group 3 (HM-). Further, segments with EDWT<4mm were defined as myocardial scar (scar). Finally, patients were classified into four groups by the extent of HM (%LV) and scar segments: Group A (HM≤10% and scar<2 segments); Group B (HM≤10% and scar≥ 2 segments); Group C(HM>10% and scar<2 segments); Group D(HM>10% and scar≥2 segments). All-cause death was defined as the primary endpoint. The cumulative survival curve was constructed using the Kaplan-Meier analysis and were compared with the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was used to determine independent predictors for all-cause death.
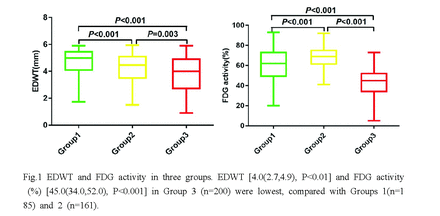
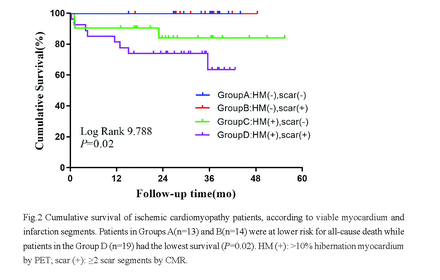
Results: RESULTS: Moderate-strong correlations were observed for EDV (r=0.916,P<0.001; r=0.631, P<0.001; r =0.575, P<0.001), ESV (r = 0.906,P<0.001; r =0.673, P<0.001; r =0.594, P<0.001), EDVI (r=0.903,P<0.001; r =0.639, P<0.001; r=0.576, P<0.001), ESVI (r=0.903,P<0.001; r =0.639, P<0.001; r=0.576, P<0.001) and LVEF r=0.615,P<0.001; r=0.675, P<0.001; r=0.528, P<0.001) among GSPECT, GPET and CMR, respectively. As depicted in Fig.1, EDWT [4.0(2.7,4.9), P<0.01] and FDG activity (%) [45.0(34.0,52.0), P<0.001] in Group 3 (n =200) were lowest, compared with Group1 (n=185) and Group 2 (n=161). Only a weak correlation was observed for EDWT and FDG activity in Group 3 (r=0.247,P<0.001) but not in Groups 1 and 2. During follow-up, 11(14.7%) patients suffered from all cause death. LVEF by GSPECT had no significant difference among 4 groups [22.0(16.5,31.0) vs.19.0(15.0,24.5) vs.19.0(15.0,25.5) vs.18.0(13.0,25.0), P=0.60]. As shown in Fig.2, patients in Groups A (n=13) and B (n=14) were at lower risk for all-cause death while patients in the Group D (n=19) had the lowest survival (P=0.02). On multivariate cox regression analysis, combination of HM by PET and scar by CMR was the only independent predictor for all-cause death (HR=3.961,95%CI:1.289-12.172, P=0.016).
Conclusions: CONCLUSION: Combination of HM by PET and wall thickness by CMR could improve the risk stratification in patients with ICM. This finding warrants further investigations.