Abstract
3340
Introduction: Remote ischemic conditioning (RIC) has recently emerged as a potential novel therapeutic strategy to achieve protection against acute myocardial infarction (AMI) injury. We aimed to evaluate the longitudinal effects of RIPostC on AMI using multiple radionuclide imaging in pigs.
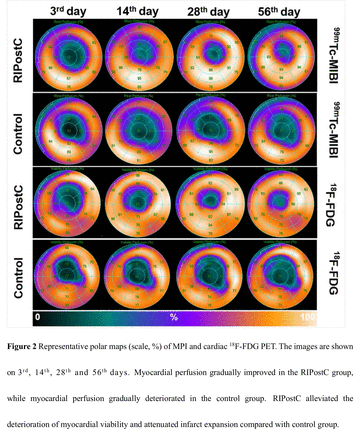
Methods: AMI was induced by placing an embolus into 1 to 2 mm under the first anterior descending branch in 12 animals. In the experimental group, remote ischemic conditioning was induced in pigs by blood pressure inflation on the lower limbs for 5-min period and 4 cycles after AMI. A series of gated 99mTc-MIBI myocardial perfusion SPECT/CT (G-SPECT) imaging and gated 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging (G-PET) were performed longitudinally at 3rd, 14th, 28th and 56th day after AMI. Total perfusion defect (TPD, %), hibernating myocardium (HM, %), scar myocardium (%), LV global function (LVEF, %), LV remodeling (EDV, ESV) and regional function (wall motion and wall thickening) were calculated and analyzed. And bone marrow metabolic activity were analyzed, and inflammation biomarkers matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) were measured.The minipigs were euthanized in the last time point.The differences of indexes between groups at different time points were assessed. Independent-samples t test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the changed values (Δ value,each time point subtracted the 3rd day) of multiple parameters. Differences were considered significant at the level of P<0.05.
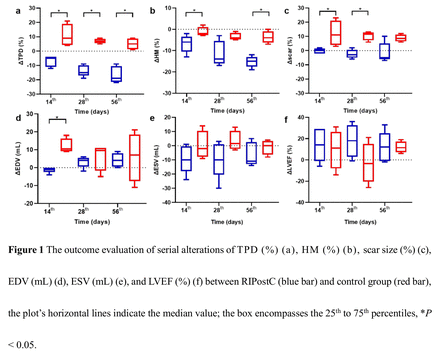
Results: In outcome evaluation, there was a significant attenuation in TPD (Δ value, at 14th, 28th and 56th days), HM (Δ value, at 14th, 56th days) and scar size (Δ value, at 14th, 28th day) in RIC animals compared with the controls (P<0.05). Additionally, RIC attenuated LV enlargement (ΔEDV, at 14th day) (-1.00 (2.50) mL vs 10.50 (7.00) mL, P=0.016) in comparison to controls. Bone marrow 18F-FDG uptake in the RIC animals was lower than the control animals ( (1.27±0.26 vs 1.67±0.18, P = 0.035) at the 3rd day after AMI.
Conclusions: Of note, RIC presented cardiac protection effects by preserving HM, attenuating infarct expansion and LV remodeling until the subacute phase post-MI, and may also have an anti-inflammatory effect at the acute phase.