Abstract
3265
Introduction: Deep learning has been applied to various processes of image reconstruction in emission tomography, including attenuation correction, scatter correction, and direct mapping from raw data to image. While each process has been investigated separately, few works investigated the performance of deep-learning based reconstruction with attenuation and scatter corrections (ASC). In here, we proposed two U-Net based models for direct SPECT reconstruction from raw data to image simultaneously with ASC, and evaluated them with patient studies.
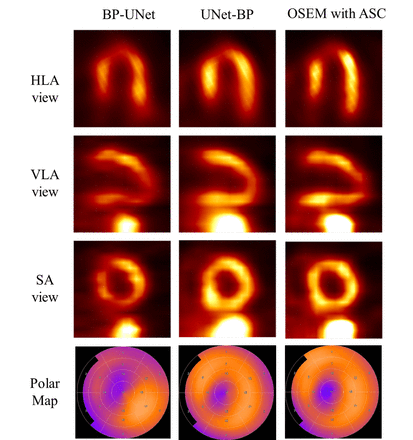
Methods: Inspired by the physical principle of filtered back-projection and back-projection filtration algorithms, we proposed to replace the conventional filters with U-Net for 2D SPECT reconstruction with ASC and thus two networks were obtained: UNet-BP, which was a U-Net followed by a back-projection operator, and BP-UNet, a U-Net following a back-projection operator, to reconstruct the SPECT image from projection of photopeak window. The loss function was consisted of L1 loss, image gradient difference and structural similarity index measure (SSIM). The training set included 91 human subjects with both cardiac SPECT with 99mTc-tetrofosmin and CT scans, whereas the testing set included 31 subjects. The SPECT projection data and conventional OSEM reconstruction images with ASC were acquired from a GE NM/CT 640 SPECT/CT scanner. The reconstruction images with the UNet-BP and BP-UNet were evaluated by using the OSEM reconstruction images as reference, by calculating the normalized mean absolute error (NMAE), SSIM and region of interest (ROI) percentage error in left ventricle (LV) myocardium.
Results: The proposed two networks generated reasonable SPECT reconstructed images with ASC as well as good quality polar maps directly from the projection data. Qualitatively, the reconstructed image and polar map with UNet-BP were more similar to those obtained from conventional OSEM reconstruction, compared to those with BP-UNet. Quantitatively, the NMAEs of the reconstructed images across the 31 testing subjects were 0.8%±0.4% and 1.1%±0.5% whiles the SSIMs were 0.91±0.04 and 0.87±0.06 for UNet-BP and BP-UNet respectively. The ROI percentage error of LV myocardium in the reconstruction images was -8.6%±8.6% with UNet-BP, and was -10.2%±16.1% with BP-UNet.
Conclusions: We proposed and evaluated two 2D U-Net-based models for direct SPECT reconstruction simultaneously with ASC from projections. Qualitative and quantitative results demonstrated that both models can generate realistic SPECT reconstruction images while UNet-BP model outperformed BP-UNet model in terms of image performance.