Abstract
3084
Introduction: PSMA-PET/CT is now widely available which has led to its use outside the often more stringent eligibility criteria of clinical trials. The objective of this study was to describe the patterns of PSMA-avid recurrent nodal disease in a large cohort of patients with biochemically recurrent (BCR) prostate cancer undergoing 18F-piflufolastat-PET/CT in routine clinical practice.
Methods: This is an IRB-approved retrospective analysis of 193 18F-piflufolastat-PET/CT scans performed at our institution between August and December 2021 to assess for BCR. A positive scan was considered when nodal metastases were described in the report impression. PSA levels and type of prior treatment were retrieved from medical records. PSA levels were categorized as < 0.2 ng/mL, ≥ 0.2 to ≤ 0.5 ng/mL, > 0.5 to ≤ 1 ng/ml and > 1 ng/mL. A radiologist reviewed all PET/CT reports to extract the nodal stations involved with PSMA-avid disease. The nodal stations were categorized according to the PROMISE classification: pelvic (external iliac, internal iliac, common iliac, obturator, presacral, perirectal), retroperitoneal and other. The presence of nodal disease was quantified and compared per type of treatment (prostatectomy [RP] versus RP + pelvic radiotherapy [RP + RT], versus RT alone) and PSA category using Fisher’s exact test. Post hoc analysis involved pairwise comparisons using the z-test of two proportions with a Bonferroni correction. A p value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
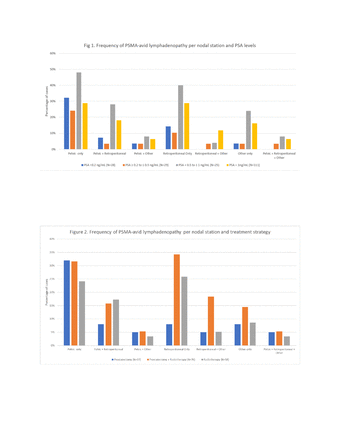
Results: A total of 160 patients (83%, 160/193) patients had a positive PSMA-PET/CT scan, of whom 52% (83/160) had PSMA-avid lymphadenopathy. PSMA-avid lymphadenopathy was seen in 36 % (10/28) of patients with PSA <0.2, 28% (8/29) with PSA ≥ 0.2 to ≤ 0.5, 68% (17/25) with PSA > 0.5 to ≤ 1, and 43 % (48/111) with PSA >1 (p= 0.022). Based on treatment strategy, PSMA-avid lymphadenopathy was observed in 35% (13/37) of patients after RP, 36% (21/58) after RT, and 50% (38/76) after RP + RT (p=0.18). The frequency of pelvic, retroperitoneal, and other lymphadenopathy per PSA level and treatment strategy is shown in Figures 1 and 2. The presence of retroperitoneal and/or other lymphadenopathy without concomitant pelvic involvement was significantly more frequent after RP + RT compared to either treatment alone (20%, 15/75 versus 3 %, 1/37 [prostatectomy] and 11% [RT]; p=0.031).
Conclusions: The detection of PSMA-avid lymphadenopathy was greater at higher PSA levels. The most frequent pattern of nodal recurrence of prostate cancer was pelvic lymphadenopathy. Retroperitoneal and other lymphadenopathy without concomitant pelvic involvement was significantly more frequent after RP + RT compared to either RP or RT alone.