Abstract
2926
Introduction: The study aims to explore whether different PET imaging protocols change the normal 18F-FDG cerebral uptake pattern acquired on an integrated TOF PET/MR system and PET/CT system.
Methods: 99 subjects with 18F-FDG PET/MR imaging and 34 subjects with PET/CT imaging for cancer screening without neurological disorders disease after health checkup aging from 25 to 75 years were retrospectively selected in this study. The subjects were divided into 4 age groups (25-39, 40-49, 50-59 and 60-75) and 3 age groups (40-49,50-59 and 60-69) for PET/MR and PET/CT, respectively. The PET scans were performed after about 30 or 60 min FDG injection and about 60 min for PET/MR and PET/CT, respectively. The brain scan durations were 6 min and 3min for PET/MR and PET/CT according to the vendor suggested protocols. All the PET images were reconstructed by TOF+PSF OSEM algorithms with default settings. The Q. Brain (GE Healthcare) combined with the in-house registration protocol was used to register the brain to the ICBM 152 brain template. The average SUV (SUVave) ratios (SUVR) to pons and cerebellum and 26 region SUVave in cerebral cortex were extracted. The cerebral uptake patterns were also visually evaluated. Student’s t-test and percent differences were applied to examine the SUV and SUVR variances at brain cortex regions between PET/MR and PET/CT, and between two scan time points.
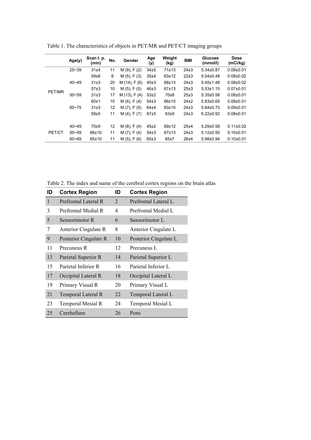
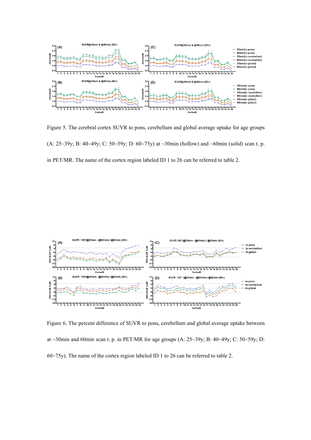
Results: The 18F-FDG cerebral uptakes in the 26 cortex regions for the highest to the lowest are: primary visual > posterior cingulate, precuneus, occipital lateral > prefrontal lateral > prefrontal medial, sensorimotor, parietal superior, parietal inferior > anterior cingulate, temporal lateral, cerebellum > temporal mesial > pons, which were consistent in PET/MR and PET/CT with difference less than 3%. Greater variances for SUVR to pons or cerebellum were observed in the regions at the older groups (~6.5% difference to cerebellum for 60 years or above, ~7% difference to pons for 50 years or above) while errors of SUVR to global average uptake was relatively small (<5%). In comparison with imaging at 30min post-injection, SUVR to global average uptake were also in good consistent except for temporal mesial, cerebellum and pons at 25+years group with larger percent differences. Besides, large difference were observed for SUVR to pons at 25+ years group and to cerebellum at 25+y and 60+y groups between two scan time points.
Conclusions: Different PET imaging protocols (varying scanner and scan duration) does not significantly change the 18F-FDG cerebral uptake pattern with a greater variance for the elder groups. Post-injection time has effects on the SUVR patterns, especially on the SUVR to pons and cerebellum and on the younger adults’ group.