Abstract
2897
Introduction: Background and purpose: Heavy alcohol drinking-induced alcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis and early-stage alcoholic liver fibrosis may progress to advanced-stage alcoholic liver fibrosis(AALF)/cirrhosis which is incurable due to lack of non-invasive imaging technique for diagnosis of collagenogenesis in activated hepatic stellate cells(HSCs) at the early reversible stage. Proline has been known as the most abundant amino acid of collagen type 1 synthesized by activated HSC with transportation of proline transporter. cis-4-[18F]fluoro-L-proline([18F]fluoro-proline) was reported as a useful tool to quantify collagenogenesis in experimental alcoholic steatohepatitis. The present study is to use [18F]fluoro-proline microPET non-invasive imaging to quantify liver collagenogenesis in HSC of experimental AALF.
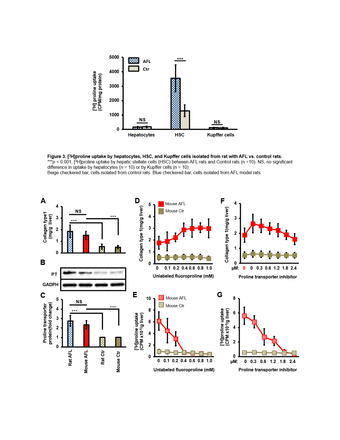
Methods: Methods: AALF model was set up by modified Lieber-DeCarli liquid ethanol diet for 12 weeks along with intraperitoneal injection(ip) of CCl4(0.5ml/kg) during 5~12th week. Controls were fed isocaloric liquid diet and ip. PBS. In vitro [3H]proline uptake by HSCs isolated from livers was quantified using liquid scintillation counter and collagen type 1 production in HSCs culture medium was assayed by ELISA. Ex vivo liver collagen type 1 and proline transporter protein were compared between AALF rats and mice. [3H]proline uptake specificity in ex vivo liver tissues was tested using unlabeled proline and transporter inhibitor benztropine at different doses. Liver H&E, trichrome stain and blood biochemistry were tested in rats and mice. In vivo dynamic and static [18F]fluoro-proline microPET/CT was done to quantify tracer uptake in AALF mice.
Results: Results: In vitro HSCs study showed significant higher [3H]proline uptake(23007.9±5089.2 vs. 1075.4±119.3CPM/mg, p<0.001) in HSCs isolated from ALF rats than controls and so was collagen type 1 production(24.3±5.8 vs. 3.0±0.62 mg/ml, p<0.001) in HSCs culture medium. Highly positive correlation between [3H]proline uptake and collagen type 1 by HSCs of AALF rats was found(r value=0.92, p<0.01).
Ex vivo liver tissue study showed no significant difference in collagen type 1 levels between AALF rats (14.83±5.35mg/g) and AALF mice(12.91±3.62mg/g, p>0.05), so was proline transporter expression between AALF rats(7.76±1.92-fold) and AALF mice(6.80±0.97-fold). Unlabeled fluoro-proline induced generation of liver tissue collagen type 1 and [3H]proline uptake were specifically blocked by transporter inhibitor.
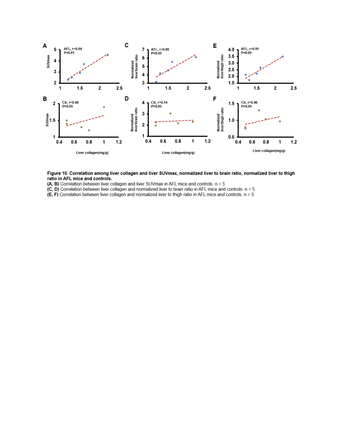
In vivo [18F]fluoro-proline microPET/CT imaging showed higher SUVmax in liver(4.90±0.91vs. 1.63±0.38, p<0.01), higher normalized liver/brain ratio(12.54±0.72 vs. 2.33±0.41, p<0.01), and higher normalized liver/thigh ratio(6.03±0.78 vs. 1.09±0.09, p<0.01) in AALF mice than controls, which are all positive correlated with fluoro-proline-induced levels of collagen in liver tissue(r value≥0.93, p<0.01) in AALF mice, but not correlated with existing liver collagen.
Liver histology showed increased collagen in liver of AALF mice, and blood ALT and AST levels were also much higher in AALF mice than controls, but not significant different in blood fibrotic parameters HA, A2M, TGFβ1 and MMP1.
Conclusions: Conclusions: [18F]fluoro-proline microPET/CT fails to quantify existing liver collagen in AALF mice but may be useful to visualize collagenogenesis in activated HSC of experimental AALF, which is limited for use in the advanced-stage alcoholic live fibrosis/cirrhosis.