Abstract
2894
Introduction: Lung cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors, which seriously threatens human health. Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 80%-85% of total. The advent of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy has brought hope for a cure to NSCLC patients. In this paper, by preparing 124I labeled anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody, the feasibility of using it as a PD-L1 targeting molecular probe was discussed.
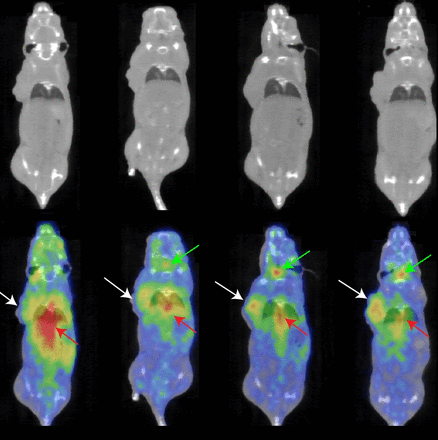
Methods: Methods: The expression of PD-L1 in NSCLC cell lines was detected by Western Blot, quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and flow cytometry. 124I and anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody Durvalumab were labeled in Iodogen tubes and purified by PD-10 column, and the radiochemical purity was determined. Probe stability was measured in PBS buffer and FBS for 72 h, respectively. Twenty-four H460 tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into 6 groups, 124I -Durvalumab was injected via tail vein at 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 120 h, and 180 h after injection, respectively. Collect organs and tissues, analyze the radioactive uptake of each organ and tissue, and analyze the target-to-substantial ratio. Another 3 tumor-bearing mice underwent micro-PET imaging 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 120 h after probe injection.
Results: Western blot, qPCR and flow cytometry results showed that human NSCLC cell line H460 highly expressed PD-L1. After purification, the radiochemical purity of 124I -Durvalumab was greater than 95%. The probe was stable in PBS buffer and fetal bovine serum, and the radiochemical purity was still above 85% after 72 hours (PBS: 87.18%, FBS: 85.16%). In the biodistribution experiment, the radioactive uptake of the tumor did not change significantly (12h: 4.28±0.20 %ID/g; 24h: 4.92±0.32 %ID/g; 48h: 5.16±0.71 %ID/g; 72h: 4.81±0.47 %ID/g; 120h: 4.87±0.83 %ID/g; 180h: 4.78±0.55 %ID/g), while the radioactive distribution in blood gradually decreased. The ratios of non-target organs such as muscle and liver gradually increased with time. Micro-PET imaging showed similar performance.
Conclusions: 124I-labeled Durvalumab has high stability in vitro and in vivo, and has a strong binding force to the PD-L1 target. Biodistribution experiments in tumor mice and Micro-PET imaging were demonstrated.