Abstract
2873
Introduction: Basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) is an invasive subtype of breast cancer with a worse prognosis and unique morphological characteristics. Lack of specific biomarkers makes it extremely difficult for accurate diagnosis in the early stage and specific targeted therapy. Consequently, it is particularly important to find specific biomarkers. Cytokeratin-14 (CK14), also known as keratin 14, is mainly expressed in the basal layer of stratified squamous epithelium. It has a critical role in maintaining cell morphology and resisting external mechanical stress. High levels of CK14 have been found in multiple types of tumors, especially in BLBC. In our study, an anti-CK14 monoclonal antibody was successfully produced, purified, and labeled with 99mTc to evaluate the feasibility of visualizing the CK14 level in BLBC.
Methods: The anti-CK14 monoclonal antibody was generated through hybridoma technology and conjugated with succinimidyl 6-hydraziniumnicotinate hydrochloride. The radiolabeling efficiency and the stability of 99mTc-HYNIC-Anti-CK14mAb were determined using instant thin layer chromatography. MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 cells were selected. The in vitro binding specificity of the tracer to CK14 was validated by immunofluorescence, cell uptake and internalization experiments. Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan was performed in tumor-bearing nude mice at 6h, 12h, 24h. Biodistribution study were consistent with SPECT imaging, and the tumor/muscle (T/M) and tumor/blood (T/B) ratio were calculated.
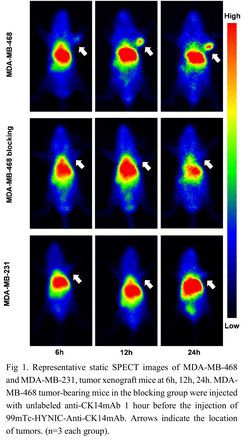
Results: Anti-CK14mAb was successfully prepared. The radiolabeling yield of 99mTc-HYNIC-Anti-CK14mAb reached 73.58 ± 5.35% (n=3) with specific radioactivity at 528.36 MBq/nmol. Higher CK14 levels were found in MDA-MB-468 cells and tumors when compared with that of MDA-MB-231 cells and tumors as revealed by western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Cell uptake experiments demonstrated a rising trend with time in MDA-MB-468 cells. The uptake ratio increased from 0.535% ± 0.053% (1 h) to 1.568% ± 0.247% (6 h). In contrast, the uptake rate in the blocking group cells was much lower (0.441%–0.557%) at 6 h. These results verified the specific binding of 99mTc-HYNIC-Anti-CK14mAb to CK14+ MDA-MB-468 cells. Internalization assays indicated the tendency of internalization ratio of MDA-MB-468 cells was similar to the tendency of total cell uptake ratio. The ratio of internalization to total cell uptake (internalization + membrane bound) increased from 51.39% ± 3.51% at 1 h to 76.39% ± 3.65% at 6 h. These results were consistent with the fact that CK14 was mainly distributed inside the cells. On the SPECT images, higher radioactivity accumulation was observed in MDA-MB-468 tumors than in MDA-MB-231 tumors, at 6h, 12h, 24h post injection of the tracer. Biodistribution study demonstrated the radioactivity accumulation in MDA-MB-468 tumors (14.245 ± 3.410 %ID/g) was significantly higher than that of MDA-MB-231 tumors (6.585 ± 0.586 %ID/g) and blocking group (injected with 100 times excess antibodies, 7.361 ± 0.657 %ID/g). Moreover, the tumor to blood ratios (T/M 18.18 ± 7.613 vs 6.352 ± 1.347 vs 7.980 ± 2.038) and tumor to blood ratios (T/B 1.702 ± 0.613 vs 0.611 ± 0.085 vs 0.6797 ± 0.1637) of the MDA-MB-468 group were significantly higher than that of the blocking group and MDA-MB-231 control group, demonstrating the good affinity and specificity of 99mTc-HYNIC-Anti-CK14mAb for targeting BLBC tumor.
Conclusions: We developed a molecular probe 99mTc-HYNIC-Anti-CK14mab targeting CK14 with high affinity and specificity to MDA-MB-468 tumors, making it a potential imaging tool for the diagnosis of CK14 overexpressing BLBC. In the future, the developed tracer may also provide valuable information to help determine which patients are suitable for anti-CK14 therapy.