Abstract
2605
Introduction: Amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition is one of the earliest detectable brain changes in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis. In clinical practice, brain amyloid can be measured using positron emission tomography (PET) to assess Aβ status in patients being evaluated for AD or other causes of cognitive decline. Trained readers categorise PET scans as either Aβ positive or negative based on visual inspection. However, adjunct quantitative analysis of brain Aβ PET imaging is becoming more widely available in both clinical and research settings where a number of regulatory approved software packages can generate standardised uptake value ratios (SUVr) and calculate individual Z-scores. Therefore, it is of direct value to the wider neurology and imaging communities to assess the compatibility of clinically available software packages. In this work, composite SUVr for [18F]flutemetamol PET is compared across four regulatory approved software packages. Each software package assessed offers individual features but this collaborative project aimed to investigate the compatibility of a central and standardized measure, composite cortical SUVr with the intention of increasing visibility, understanding and translation of clinically relevant quantitative methods. Our hypothesis was that all software packages assessed would provide highly correlated quantitative results (composite SUVr) according to interclass correlation coefficient, percentage agreement around a positivity threshold and kappa scores.
Methods: Composite SUVr using the pons as the reference region were generated from [18F]flutemetamol PET in a retrospective cohort of 80 amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients (40 each male/female; mean age=73y). Based on previous autopsy validation work (Thurjell et al 2014), an Aβ positivity threshold 0.6 SUVr was applied. Quantitative results from four software packages were assessed:
MIM Software’s MIMneuro (https://www.mimsoftware.com/nuclear_medicine/ mim_neuro) Syntermed’s NeuroQ (https://www.syntermed.com/neuroq) Hermes Medical Solutions’ BRASS (https://www.hermesmedical.com/neurology/) GE Healthcare’s CortexID (https://www.gehealthcare.com/courses/aw-cortex-id)
Statistical analysis
Percentage agreement was calculated across all software packages using an Aβ positivity threshold of 0.6 SUVr. Group-wise correlation (intraclass correlation coefficient-ICC) on composite SUVr was measured for all software packages. Kappa scores were calculated to assess inter-rater reliability of binary clinical decision between each pair of software packages (Cohen’s) and group-wise (Fleiss’). Company names have been blinded when reporting results.
Results: AgreementWith a 0.6 SUVr positivity threshold, 95% agreement was achieved across the software packages. Two patients were narrowly classed as positive by one software package but negative by the others, and two patients vice versa.
Reliability
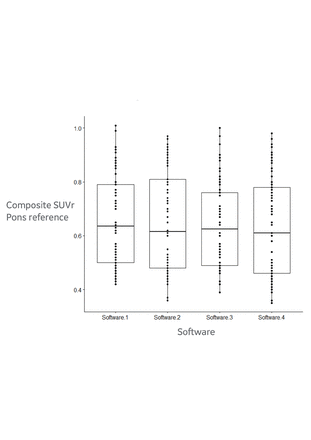
Excellent reliability was found between composite SUVr measurements for all four software packages, see figure 1 showing boxplots for each software. The average measure ICC was 0.97 with 95% confidence interval from 0.957 to 0.979.
All kappa scores were ≥ 0.9 signifying “almost perfect” inter-rater reliability. Fleiss’ Kappa for the 4 software packages together was 0.948. Cohen’s Kappa for individual pairs was as follows:
Software 1 vs 2 = 1 Software 1 vs 3 = 0.92 Software 1 vs 4 = 0.97 Software 2 vs 3 = 0.92 Software 2 vs 4 = 0.97 Software 3 vs 4 = 0.90
Conclusions: Regulatory approved software packages provide highly correlated and reliable quantification of [18F]flutemetamol amyloid imaging data with a 0.6 SUVr positivity threshold when using the pons as a reference region. Similar analysis is encouraged using other tracers and reference regions, as well as the Centiloid scale when implemented by more software packages.