Abstract
2568
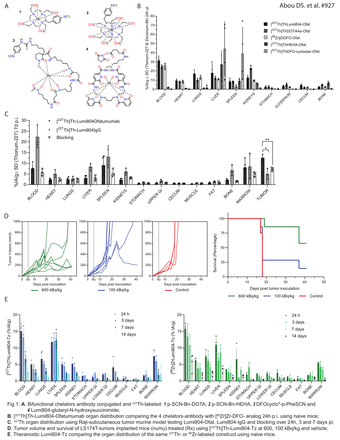
Introduction: Thorium-227 is a promising radioisotope for targeted alpha particle therapy of disseminated and bone cancers. It produces 5 alpha particles through its decay chain, and its first daughter is formulated in the clinically approved Radium-223 dichloride. There is an ample supply of 227Th allowing for clinical use, however the chemical challenges of chelating this large, tetravalent f-block metal cation are considerable. Here, we aim to achieve a stable chelation of 227Th4+ for alpha particle emitting radioimmunotherapy. We compare four bifunctional chelators with known affinity for thorium: p-SCN-Bn-DOTA 1; p-SCN-Bn-HEHA 2; DFOcyclostar-p-Phe-SCN 3 and Lumi804-NHS 4 (Fig. 1A). All chelators were conjugated to antibodies and evaluated for in vitro stability. The most stable leads were tested in vivo for organ distribution, tumor targeting and therapeutic efficacy. Lumi804 complexing the positron emitting 89Zr was also investigated as a radiotracer for imaging.
Methods: 227Th-antibody labeling was pursued following a 1-step reaction except for DOTA, achieved in a 2-step procedure. Each construct has been evaluated utilizing thin layer chromatography and fast performance liquid chromatography followed by gamma counting using NaI and high purity germanium detection. All 227Th-antibodies were checked in vitro utilizing human serum challenge and underwent in vivo organ distribution using naïve mice. We conjugated the chelators to ofatumumab (Ofat), targeting CD20 and trastuzumab (Tz) targeting epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The resulting conjugates were tested on Raji B-cell lymphoma and LS174T colon cancer murine models, respectively. Lumi804-Tz was also radiolabeled with 89Zr, as a theranostic pair of 227Th. Comparative organ distribution in naïve mice was undertaken.
Results: All Ofat-chelator conjugates were successfully synthesized and 227Th-labeled were purified to a radiochemical purity >95%. [227Th]Th-HEHA-Ofat showed moderate in vitro stability with 50% decomplexation over 24 h in serum plasma challenge and similar effect in vivo with high liver and bone uptake. DFOcyclostar-Ofat presented excellent labeling efficiency and in vitro stability (>95% bound 227Th over 7 days), however in vivo resulted in high liver and spleen uptake, indicative of aggregation. [227Th]Th-DOTA-Ofat labeled with poor yields (≤5%), low specific activity (0.08 GBq/g) and modest in vitro stability (<80% over 7 d), though the organ distribution in naïve mice was similar to that of [225Ac]Ac-DOTA- and [89Zr]Zr-DFO- analogs ( Fig.1B).
Regardless of 223Ra pre-purification, Lumi804 presented great abilities to coordinate 227Th when conjugated to Ofat, igG or Tz with yields ranging from 40 to 97% depending on the antibody. The radiochemical purity was consistently >95% and specific activity reached 8GBq/g. The serum challenge showed >85% of 227Th bound after 7 days. In vivo tumor-targeting of [227Th]Th-Lumi804-Ofat was confirmed with accumulation in Raji-tumors at 3 days and 7 days (20 and 15% IA/g) at least double that of igG (7%IA/g) and blocking (7%IA/g) (Fig. 1C).
We further validated therapeutic efficacy using Tz targeting the HER2 expressing LS174T colon cancer model. [227Th]Th-Lumi804-Tz demonstrated potency at 600 kBq/kg indicating tumor growth inhibition and extended survival (p<0.05) as compared to vehicle (Fig. 1D). The PET tracer analog, [89Zr]Zr-Lumi804-Tz showed organ distribution similar to that of 227Th, confirming the 89Zr/227Th theranostic capability with the Lumi804 chelator (Fig. 1E).
Conclusions: Stable 227Th chelation was demonstrated. Out of four chelators tested, Lumi804 is the most stable and versatile chelator permitting facile coordination of 227Th and 89Zr across several antibody conjugates. Importantly, we demonstrated tumor growth inhibition and extended survival using an aggressive human tumor model in mice. These data support the development of 227Th radioimmunotherapy for theranostic application.