Abstract
2314
Introduction: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are native brain receptors that are vital for learning and memory functions. In particular, GluN2B subunit-enriched NMDARs are involved in several neurodegenerative and psychological diseases. Recently, we successfully performed a first in-human evaluation of (R)-11C-Me-NB1 in healthy volunteers. In this work, we evaluated the enantiomers of 18F-OF-NB1 in rodents. Following the initial literature report, we further evaluated the binding of 18F-OF-NB1 in multiple sclerosis (MS) post-mortem brain tissues.
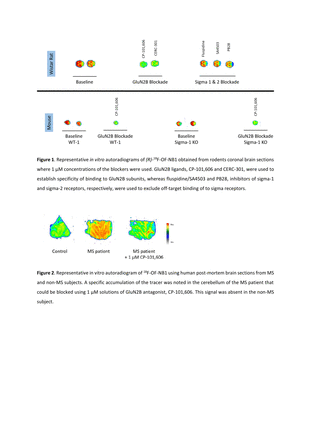
Methods: 18F-OF-NB1 was synthesized over two steps starting from an iodonium precursor, followed by chiral separation of the racemic mixture to obtain the (R)- and (S)- enantiomers. Both enantiomers were evaluated in an in vitro autoradiography on brain slices from healthy rodents and sigma-1 knockout mice using the GluN1/2B ligands CP-101,606 and CERC-301, and the sigma ligands fluspidine, SA4503 and PB28 as blockers. Furthermore, the enantiomers were evaluated by PET imaging and whole-body ex vivo biodistribution studies in Wistar rats using CP-101,606 (1 and 5 mg/kg) and eliprodil (2 mg/kg) as blockers, respectively. Finally, the tracer accumulation in post-mortem human brain tissues - cerebellum and cortex - of a healthy subject and an MS patient was evaluated.
Results: The radiochemical conversion of 18F-OF-NB1 was 21 ± 1.6% (n=3) which was comparable between the metal-free strategy using an iodonium precursor and the previousely used copper-catalyzed boronic ester precursor. At the end of the radiosynthesis, chiral purification resulted in enantiopure tracers with an ee value of >98% for each enantiomer. In rodent autoradiographic experiments, (R)-18F-OF-NB1 showed higher specificity than the (S)-enantiomer (72% vs 51% blockade, respectively) whereas in PET imaging experiments, both tracers showed high uptake in GluN1/2B-rich regions such as the cortex, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus. The (R)-enantiomer, however, showed higher overall brain uptake and considerably slower washout kinetics compared to (S)-18F-OF-NB1. Dose-dependency of both enantiomers was established using two doses of GluN1/2B ligand CP-101,606, although the dependency was more delineated in the case of (R)-18F-OF-NB1. In concert with the PET results, the ex vivo biodistribution study showed higher uptake of the (R)-18F-OF-NB1 than the (S)-enantiomer in the rat brain. In post-mortem human brain tissues, 18F-OF-NB1 exhibited specific accumulation in MS cerebellum slices whereas this accumulation was absent in healthy control cerebellum.
Conclusions: (R)-18F-OF-NB1 is a promising radioligand for the in vivo imaging of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors and a frontrunner candidate for clinical translation. Furthermore, it offers potential prognostic value as a biomarker in MS patients.