Abstract
1544
Objectives: Noninvasive functional imaging using PET is the ultimate technique for the visualization and quantification of events at the cellular and molecular levels. Reducing the injected activity and/or the scanning time is a desirable goal to minimize radiation exposure and/or maximize patients’ comfort. To achieve this goal, we developed a deep neural network (DNN) model for synthesizing full-dose (FD) time-of-flight (TOF) bin sinograms from their corresponding fast/low-dose (LD) TOF bin sinograms.
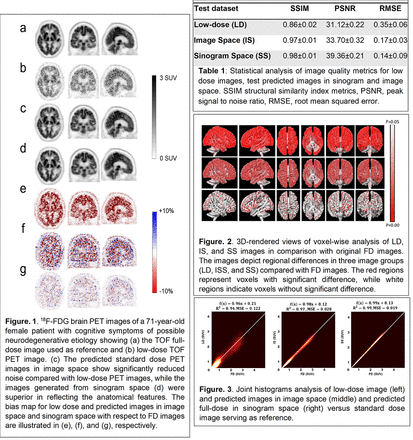
Methods: Clinical brain PET/CT raw data of 140 normal and abnormal patients were employed to create LD and FD TOF bin sinograms. The LD TOF sinograms were created through 5% undersampling of FD list-mode PET data. The TOF sinograms were split into seven time bins (0, ±1, ±2, ±3). Residual network (ResNet) algorithms were trained separately to generate FD bins from LD bins. An extra ResNet model was trained to synthesize FD images from LD images to compare the performance of the DNN in sinogram space (SS) vs implementation in image space (IS). Comprehensive quantitative and statistical analysis was performed to assess the performance of the proposed model using established quantitative metrics, region-wise standardized uptake value (SUV) bias and statistical analysis of 83 brain regions.
Results: The absolute average SUV bias was 0.96 ± 0.95% and 1.40 ± 0.72% for SS and IS implementations, respectively. The joint histogram analysis revealed that the lowest mean square error (MSE) and highest correlation (R2 = 0.99, MSE = 0.019) were achieved by SS compared to IS (R2 = 0.97, MSE= 0.028). Conclusions: The results demonstrated that images reconstructed from the predicted TOF FD sinograms using the SS approach led to higher image quality and lower bias compared to images predicted from LD images.