Abstract
65
Objectives: Perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) are persistent environmental pollutants that have the potential to accumulate in biological systems and tissues. PFAS are also known to negatively impact human health1, and are an emerging contaminant of concern in drinking water worldwide2. Recently, our group reported on the first use of radiolabeled [18F]PFAS for the study of kinetics of these compounds in mice.3 The objective of this work was to apply this technique to study the real-time uptake of [18F]-labeled PFAS compounds, perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA or C8) and perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA or C6) in pregnant mice as well as the placental trafficking within one hour of injection.
Methods: [18F]C8 and [18F]C6 were prepared as described previously.3 Pregnant mice at 17-19 days of gestation were anesthetized and administered 350 mgI/kg of omnipaque (CT contrast agent) via tail vein followed by 4.4 MBq (~120 µCi) of either [18F]C8 or [18F]C6 in 100 µL of saline. Animals underwent dynamic PET imaging for 20 min, followed by a 5 min CT and a second, 40 min dynamic PET acquisition. After imaging, the mice were sacrificed for biodistribution and organs were collected, weighed and assessed for radioactivity. Quantitative image analysis was conducted to examine the dynamic uptake in placenta, fetuses and maternal organs.
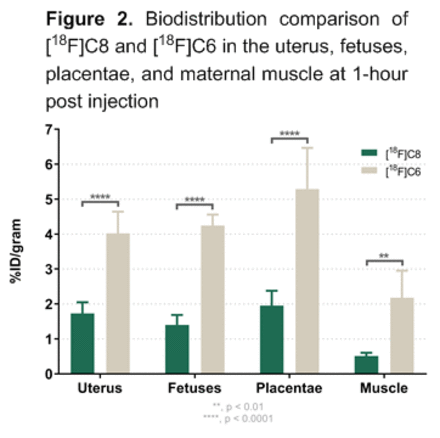
Results: [18F]C8 and [18F]C6 were labeled with ~14% and ~30% yields, respectively and high purity, >99%. In vivo biodistribution studies showed uptake in all organs tested, with non-significant difference in levels of tracer activity in most organs/tissues tested. Uptake of the tracer in the uterus, placentae and fetuses were statistically significant between the C8 and C6 tracers at 1.7 + 0.3 %ID/g vs 4.1 + 0.6 %ID/g, 1.4 + 0.3 %ID/g vs 4.2 + 0.3 %ID/g and 2.0 + 0.4 %ID/g vs 5.3 + 1.1 %ID/g, respectively. SUV analysis and time activity curves of the tracer uptake over time show a distinct high uptake in the placentae and clear transport into the fetuses over time for [18F]C8 and[18F]C6.
Conclusions: Our work shows a statistically higher uptake of [18F]C6 compared to [18F]C8 in tissues including the uterus, fetuses, placentae and maternal muscle. PET imaging confirmed high [18F]PFAS transport into the fetus within one hour of injection into the bloodstream. Work is ongoing with other [18F]-labeled PFAS to assess structure activity relationships and potential transport mechanisms. This method can be used to estimate relative fetal exposure risks to various PFAS. References. 1. Sunderland, E.M., Hu, X.C., Dassuncao, C., Tokranov, A.K., Wagner, C.C. and Allen, J.G., A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Exposure Sci. & Environ. Epidemiology, 2018, Nov 23:1. 2. Guelfo, J.L. and Adamson, D.T., Evaluation of a national data set for insights into sources, composition, and concentrations of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in US drinking water. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 236, 505-513. 3. Burkemper, J. L.; Aweda, T. A.; Rosenberg, A. J.; Lunderberg, D. M.; Peaslee, G. F.; Lapi, S. E., Radiosynthesis and Biological Distribution of 18F-Labeled Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances. Environ Sci Technol Lett 2017, 4 (6), 211-215.