Abstract
612
Objectives: The L-type amino acid transporter-1 (LAT1) is upregulated in many primary and metastatic prostate cancers making it an ideal target for both imaging and therapy. LAT1 preferentially transports α-amino acids with large neutral side chains through an influx/efflux exchange mechanism. Radiolabeled amino acids, [18F]FET and [18F]Fluciclovine that act as transport substrates have been used to target LAT1 and ASCT2, a glutamine transporter, respectively. [18F]Fluciclovine is FDA approved for imaging prostate cancer, thus was used as a clinically relevant imaging agent for comparison. [18F]FET shows low tumor to normal tissue ratios outside the brain due to lack of adequate selectivity for LAT1 over other system L transporters and its bidirectional transport which limits concentrative levels. In contrast, antibody-based agents can achieve very high selectivity for LAT1 and may distinguish between aggressive and more indolent forms of prostate cancer. In this study, we imaged varying LAT1 protein levels in animal models of prostate cancer (DU145, 22RV1 and LNCAP) using [89Zr]DFO-α-LAT1 antibody and compared the uptake to the radiolabeled amino acids, [18F]FET and [18F]Fluciclovine. The LAT1 levels in the cell lines were also measured and compared with western blot and flow cytometry.
Methods: Anti-LAT1 antibody was modified with DFO at 4:1 molar excess of DFO chelate to protein in 0.1M sodium carbonate, pH 9. The DFO antibody conjugate was radiolabeled with 89Zr in 1 M HEPES, pH 7.2 at 0.22 GBq/mg. Analysis of immunoreactive fraction of the radiolabeled antibody in HCT116 cells (high LAT1 expression) was performed. LAT1 expression levels in prostate cell lines were determined via flow cytometry. Cellular uptake and internalization of [89Zr]DFO-α-LAT1 were performed at 37°C in DU145, 22RV1 and LNCAP cells at different time points. PET imaging and ex vivo biodistribution were done in xenograft mice models of DU145, 22RV1 and LNCAP injected with 3.7 - 4.4 MBq of [18F]FET or [18F]Fluciclovine and [89Zr]DFO-α-LAT1.
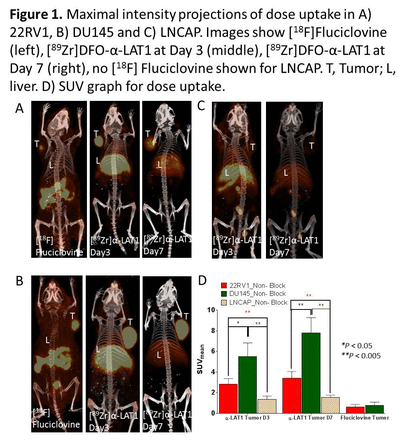
Results: The DFO antibody conjugate was radiolabeled with 89Zr at specific activities of 0.21 ± 0.09 GBq/mg and radiochemical purity of ≥95%. The immunoreactive fraction was ≥80%. Flow cytometry and cell uptake studies showed that the highest and lowest expression of LAT1 was observed in DU145 and LNCAP respectively. [89Zr]DFO-α-LAT1 was rapidly taken up with 57%, 63% and 31% internalized at 10 min incubation by DU145, 22RV1 and LNCAP cells respectively. Ex vivo biodistribution at day 7 in mice xenografts showed higher uptake values of [89Zr]DFO-α-LAT1 in DU145 (41.8 ± 2.4 %ID/g ), 22RV1 (25.6 ± 2.8 %ID/g) as compared to LNCAP (4.4 ± 0.4 %ID/g). In contrast, low tumor accumulation was observed for [18F]FET (0.6 ± 0.2 %ID/g) and [18F]Fluciclovine (0.8 ± 0.3 %ID/g) in DU145 tumors. SUV analysis of PET images confirms that the highest accumulation was observed in DU145 vs LNCAP, 2.8 ± 1.0 vs. 1.2 ± 0.2 at day 3 and 4.4 ± 1.3 vs. 1.1 ± 0.1 at day 7. Conclusions: Anti-LAT1 antibody showed high selectivity for LAT1 and distinguished between low and high expressing LAT1 prostate tumors. Higher tumor accumulation with superior tumor to background ratios at all time points of [89Zr]DFO-α-LAT1 was observed in the tumor models as compared to [18F]FET or the clinically available amino acid PET tracer [18F]Fluciclovine. Use of 89Zr with its relatively long half-life for immnuoPET imaging in tumor models allowed high contrast images to be acquired up to day 7.