Abstract
302
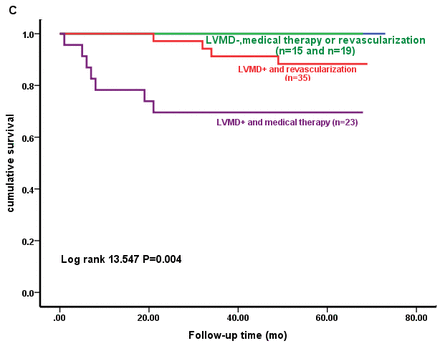
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic value of left ventricular mechanical dyssynchrony (LVMD) assessed by phase analysis of gated SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging (GMPI) in patients with LV aneurysm treated by medical therapy or revascularization. Materials and Methods: Ninety-two consecutive LV aneurysm patients (78 male, 57 ± 10 years) who underwent 99mTc-MIBI rest GMPI were retrospectively enrolled and followed-up for 57 ± 16 months. Thirty-eight patients were treated by medical therapy and fifty-four patients underwent revascularization. LVMD was analyzed by phase analysis, and parameters of BW (°), entropy (%) and SD (°) were obtained. LVMD was considered if BW ≥ 90° or Entropy ≥ 62%. Cardiac death (CD) and heart failure (HF) were defined as cardiac event during follow-up, and served as the endpoint. The patients were stratified into four groups according to LVMD and treatment strategy (medical vs. surgical). Group 1 (n=19, 21%): LVMD-, revascularization; Group 2 (n=15, 16%): LVMD-, medical; Group 3 (n=35, 38%): LVMD+, revascularization; Group 4 (n=23, 25%): LVMD+, medical. Survival curves were generated by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by the log-rank method.
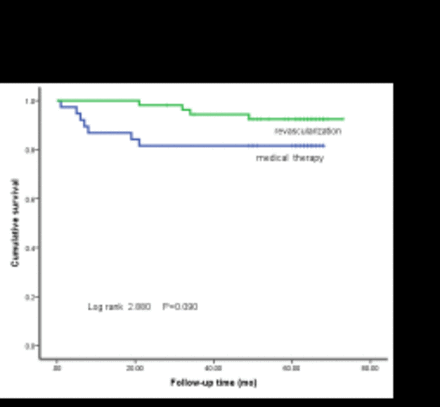
Results: 11(12%) patients suffered from cardiac death and 27(17%) patients had cardiac events. Compared with the medical group, the annual cardiac mortality (1.56% vs. 3.88%, χ2 = 2.880, P = 0.090) and the annual cardiac event rate (4.68% vs. 8.31%, χ2 = 3.796, P = 0.051) of surgical group showed a trend to be lower than medical group, but no significant difference (P>0.05). The annual mortality of the four groups (0%, 0%, 2.41% and 6.41%, χ2 = 13.55, P = 0.004) and the annual cardiac event rate (1.11%, 5.61%, 6.62%, 10.07%, χ2 = 10.20, P = 0.017) had significant difference. The annual cardiac mortality of group 3 was significantly lower than that of group 4 ( χ2 =3.94, P=0.047).
Conclusions: Patients with LV aneurysm and LVMD had a worse prognosis, coronary revascularization is associated with improved long-term survival in compared with medical therapy. In contrast, patients without LVMD had a good long-term survival, revascularization improved cardiac-event survival in comparison with medical therapy.