Abstract
1422
Objectives: Nowadays, anilino quinazoline-basedepidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinaseinhibitors (TKIs) have not only be used as targeting drugs in clinical non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treatment, but also be developed for mutant EGFR targeted radiotracers for noninvasively identifyingpatients who will benefit from EGFR-TKI. However, the key challenge is most of anilino quinazoline-based EGFR-TKIs are too lipophilic to be eliminated mainly through hepatobiliary clearance. As a result, the concentration of these TKIs in tumor is decreased which seriously affect the targeted anti-tumor effects.
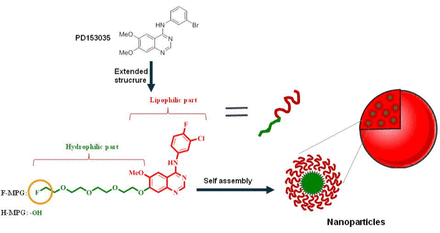
Methods: In this study, to further improve anilino quinazoline-based EGFR-TKIs qualifications and increase stability and solubility, extended structure of quinazoline ring at the 7-position with four polyethyleneglycol (PEG) chains was synthesized (F-MPG and H-MPG). We then investigatedand evaluated the drug-like properties and hepatoxicityof these two newly synthesized quinazoline derivatives.Following observations of more significant tumor inhibition was administered in cell level in vitrocompared to PD153035. We also implanted xenografts of HCC827 cells in nude mice, and used micro positron-emission tomography computed tomography (PET/CT) with 18F-FDG as tracer to image the resulting tumors in order to monitor the treatment efficacy of novel antitumor drugs.
Results: F-MPG and H-MPG compounds had been designed and synthesized and a phenomenon of F-MPG and H-MPG chemically self-assembled to nanoparticles after PEGylated was observed both in solution and in PBS. A population of vesicular structures with size between 10 and 100 nm can be seen in the F-MPG or H-MPG particles.In vitrostudies using human NSCLC cell line HCC827 show that compared to PD153035, F-MPG or H-MPGwith better water solubility inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion with high potency and induced cell cycle arrest at G0/G1phase. F-MPG or H-MPGmarkedly reduced phosphorylation of EGFR and inhibited activation of ERK and AKT. Oral administration of F-MPG or H-MPG(50mg/kg/day) to BALB/c nude mice bearing HCC827 xenografts significantly inhibited tumor growth. Importantly, F-MPG or H-MPGshowed the better safety profile with respect to variation in body weight than the PD153035 along. The PET imaging for monitoring the therapeutic efficacy also shows that tumor uptake of 18F-FDG in the F-MPG or H-MPG treated groups was significantly decreased on day 14 and 21, and even on day 21, tumors were hardly detected. Moreover, the ex vivoexperiments showed that the levels of serum biomarkers (ALT and AST) and pathological changes in liver were significantly lower than the group of PD153035.
Conclusions: In conclusion,F-MPG or H-MPGhave good drug-like properties, better anti-tumor activity, andless liver damage after PEGylated compared with PD153035 which providing solid evidence for future clinical trials. The betterantitumor activityof F-MPG or H-MPGin vitroand in vivomay be related to the extended structure-activity. On the one hand, the modified drugs with lower lipophilicity and better water solubility reduced the clearance by hepatobiliary metabolism and improved the targeting with tumor. On the other hand, it may be related to self-assembly to nanoparticles after structure modified, while the EPR effect indirectly increased drug distribution in tumor.