Abstract
1313
Objectives: The aim of this study is to prepare 64Cu-labeled Melanin nanoparticles, and to use the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect for PET/CT imaging of A431 tumor-bearing nude mice, and to evaluate its therapeutic effect.
Methods: The first part: Synthesis of PEG-MNP and completion of radiolabeling to acquire the 64Cu-PEG-MNP. The A431 cell line was selected for in vitro cell uptake and efflux experiments. In vitro stability experiments were performed in serum and saline, respectively. The second part: A431 tumor-bearing nude mice (n=8) were injected with 64Cu-PEG-MNP (11.1MBq, 300uCi) through the tail vein for PET imaging and in vivo distribution experiments. The third part: A group of A431 tumor-bearing nude mice (n=6) were treated with 64Cu-PEG-MNP (55.5 MBq, 1.5 mCi) through the tail vein, as comparison, another group (n=6) were injected with the same amount of PBS through the tail vein. After the mice were sacrificed, the tumor, liver and kidney were taken for pathological section and HE staining.
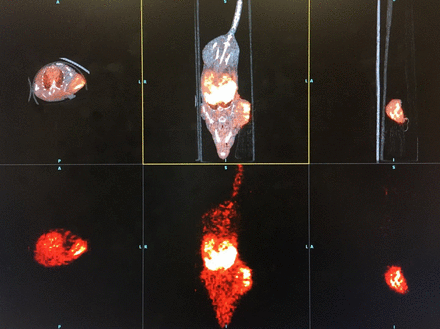
Results: The first part: We successfully synthesized PEG-MNP and explored the best labeling conditions: 300uCi and 1.5 mCi 64CuCl2 were added to 0.1 N NaOAc (pH 5.5) buffer and shaken at 40 ° C for 1 h at room temperature. Cell uptake experiments showed high uptake rates of A431 cells (peak up to 2 h), and saline stability experiments showed that the labeling rate was still >80% after 4 hours, demonstrating good saline stability. The second part:In vivo PET/CT imaging showed good tumor targeting and high intratumoral aggregation, and in vivo distribution experiments showed high uptake of the imaging agent in tumors, blood, liver, and kidney. The third part: Compared with the untreated control group, 64Cu-PEG-MNP rapidly produced a therapeutic effect on the A431 tumor-bearing mice in the treatment group. The tumor growth rate has dropped significantly. The pathological results further confirmed that the high dose of 64Cu-PEG-MNP did not produce toxicity to normal tissues.
Conclusions: The results of this study successfully demonstrated the good imaging effect of 64Cu-PEG-MNP on A431 tumors and further proved its obvious therapeutic effect. 64Cu-PEG-MNP is expected to be a promising radiolabeled probe for targeted radionuclide therapy. Key words: 64Cu; Melanin; PET/CT; Imaging agent; Radionuclide therapy