Abstract
1297
Objectives: Spectral photon counting CT has the potential to quantify low and high-risk fracture sites of osteoporotic bones, made feasible by simultaneous 3D measurements of bone microarchitecture and bone mineral density at high-spatial resolution with quantitative material information. We aimed to use photon counting spectral CT to develop a semi-automatic method to measure site-specific bone mineral density (BMD) and bone microarchitecture.
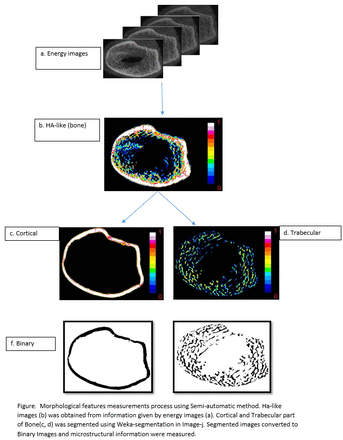
Methods: Calibration data was collected using a customised calibration phantom which included different concentrations of calcium hydroxyapatite (54.3, 104.3, 211.7, 402.3 and 808.5 mg/cm³ ) along with lipid and water, followed by scanning of ovine bone specimens. Image acquisition was performed using a preclinical MARS spectral scanner equipped with Cadmium-Zinc-Telluride assembled Medipix3RX detectors with four charge-summing mode counters (30, 45, 60 and 78 keV) at 118 kVp. Images of the biological specimens and the calibration phantom were reconstructed in narrow energy bins (30-45, 45-60, 60-78, 78-118 keV) at 90 micron voxel size and evaluated in the material domain to decompose bone-like material. Further segmentation of the cortical bone from trabecular bone was carried out on material images with Weka-segmentation using ImageJ and cortical thickness, trabecular thickness, trabecular spacing, and trabecular number were measured on segmented images. Bone mineral density was calculated in each section (trabecular and cortical) separately using customised active contouring segmentation. Semi-automatic quantitative assessment of site-specific BMD and morphological features was compared with a manual contouring technique. Intraclass correlation was conducted to calculate the correlation coefficients of these two methods on 100 anatomically identical slices.
Results: The MARS images show high-spatial resolution with quantitative material information for all bone specimens. Cortical and trabecular thickness, trabecular spacing and trabecular number were measured on segmented images. The statistical analyses showed an excellent correlation between cortical thickness values obtained with the semi-automatic method and manual method (0.99). Trabecular thickness, separation and number values showed moderate to excellent correlation between the two methods (0.60, 0.96, 0.91 respectively). Bone mineral density in each part showed consistent results with previously time-consuming manual measurements (0.90).
Conclusions: MARS spectral photon counting CT imaging is a new x-ray based imaging technology providing material specific 3D imaging at high spatial resolution. This technology has the potential to provide a quantitative method to establish imaging criteria for site-specific bone quality and fracture risk in individual bones. Semi-automatic segmentation using spectral photon counting CT gave objective bone measurements.