Abstract
1188
Introduction: The Ordered Subsets Expectation Maximum (OSEM) uses multiple iterations to provide higher quality images. The image contrast improves with a higher number of iterations, which also results in unacceptable increases in image noise. The Bayesian Penalized Likelihood (PL) reconstruction algorithm was proposed to mitigate the generation of excess noise. The Block Sequence Regularized Expectation Maximization (BSREM) algorithm was used to solve the PL equation for every single image voxel to achieve full convergence. While these methods have been demonstrated for normal clinical imaging, they have not yet been fully demonstrated for quantitative whole body dynamic (QWBD) imaging, which has potential to provide additional information beyond conventional SUV imaging. Therefore, the purpose of this work is to evaluate BSREM in comparison to conventional OSEM methods for QWBD PET imaging.
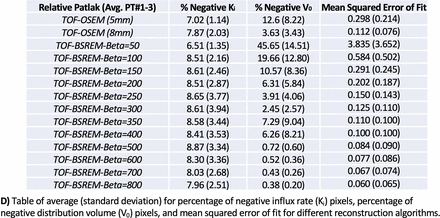
Methods: QWBD data was acquired from Discovery MI PET/CT system (GE Healthcare) using 18F-FDG as the radiotracer for three patients under IRB approval. In each patient, 6-8 whole body passes of 30 seconds each were obtained. Fourteen reconstructions were performed using OSEM and BSREM (Q.Clear) algorithms. The two OSEM reconstructions utilized 4 iterations/34 subsets/5mm smoothing and 4 iterations/34 subsets/8mm smoothing. The TOF-BSREM reconstructions were performed using penalization factors (beta) of from 50 to 800. QWBD was performed using relative-Patlak (rPatlak) (Zuo, Qi, Wang Phys Med Biol 2018 63(16)), with a relative starting time of 30 minutes, fit to a canonical arterial input function to examine the effect of the reconstruction algorithm on model fit. Influx rate (Ki, slope of the rPatlak plot) and distribution volume (V0, intercept of the rPatlak plot) were calculated using linear least squares in MATLAB. The quality of the fit was assessed using three factors: percentage of negative Ki, percentage of the negative V0, and the mean square error (MSE) of fit. Negative Ki and V0 values reflect physiologically implausible rPatlak model parameters.
Results: Using rPatlak analysis, higher filter values in OSEM results in decreases in the percent of negative offset and the mean square error of fit. Ki and the V0 images demonstrated improved appearance from an increasing beta value. With a beta=300 for BSREM, a similar rPatlak result is obtained to that of OSEM with 8mm filter. By using higher beta values in BSREM, the MSE of fit was observed to decrease, below that of OSEM with 5mm filter at beta=150 and higher, and below that of OSEM with 8mm filter at beta=350 and higher. Beta values equal to or greater than 500 also resulted in a remarkable decrease of the percentage of negative V0 values from ∼6% to less than 1%. Percent negative Ki was similar between all recons.
Conclusions: This study explores the use of BSREM reconstructions for QWBD PET applications. For beta≥500, the percentage of the negative V0 values and MSE of fit have distinct improvements. In particular for beta≥500, Ki in high blood-pool organs such as liver appear normalized and reduced relative to other recons, reflecting a more accurate fit to the rPatlak model. As demonstrated herein, PL reconstructions such as BSREM may improve the capability of QWBD, particularly when short bed times (e.g., 30 seconds) are necessary to obtain many whole body passes. Future work is necessary to explore BSREM in an expanded cohort of patients, and to further explore the capability of QWBD+BSREM to delineate disease.