Abstract
1060
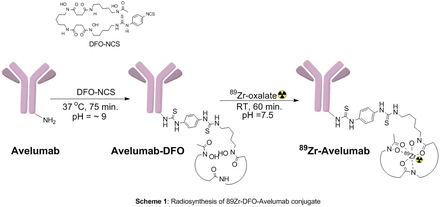
Objectives: Monoclonal antibodies radiolabeled with positron (PET) or single photon emitting (SPECT) radioisotopes serve as a tool for non-invasive quantitative imaging of tumors that can be used to detect tumors and monitor progression of therapy. Avelumab (Bavencio) is a programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) blocking antibody indicated for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) and urothelial carcinoma 1. The binding of the programmed death-ligand-1 (PD-L1) to PD-1 modifies the cells immune activity by inhibiting cytotoxic T-cells. The T-cell antitumor activity can be restored by blocking PD-L1 inhibitory receptors. The physiological mechanism for regulating immune response and T-cell activity suppression can be caused by upregulating the PD-L1 expression on various immune cells. Avelumab conjugated with 89Zr can serve as a useful imaging agent for the diagnosis of PD-L1+ tumors and monitor progression of therapy. In this abstract, we describe the radiosynthesis and qualification of 89Zr-labelled Avelumab for clinical studies (Scheme 1)
Methods: Avelumab solution pH was adjusted to ~9 using 0.1M Na2CO3. SCN-Bz-DFO (3 equivalents) was added and the mixture was incubated at 37°C for 75 minutes. The conjugate was purified on a PD10 size exclusion chromatography column using 0.9% saline. Concentration of the conjugate was determined by HPLC. 89Zr-oxalate solution (~4 mCi) was neutralized using 2M Na2CO3 to pH 7.5. To the 89Zr solution was then added saline/gentisic acid solution (0.2 mL), and 0.5M HEPES buffer (0.5mL, pH 7.2) followed by Avelumab-DFO (~1 mg) solution. The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 1 hour. Reaction completion was confirmed by iTLC. The crude product was then purified on a PD10 column using gentisic acid solution. Purified product was diluted with 0.9% saline up to 5 mL and aseptically transferred to a final product vial. Quality control analysis following USP 823 was performed on the final product. The product was tested for stability (HPLC). All six qualification runs had their bioactivity determined by immunoreactivity2.
Results: Clinical grade 89Zr-Avelumab was radio-synthesized in very high chemical (≥ 99%) and radiochemical purity (≥ 99%) in ~70% yields in high specific activity (~17 mCi/μmol). The final product passed the chemical, radiochemical, bacterial endotoxin, sterility, pH and filter integrity tests. 89Zr-Avelumab was found to be stable for 48 hours at 4oC. The immunoreactivity was >86% for all batches.
Conclusions: Clinical grade 89Zr-Avelumab (~ 1.5 mCi) was reliably and consistently radio-synthesized for six qualification runs. The product passed the quality control tests. The product was found to be stable for 48 hours at 4oC by HPLC. References: 1. Chin et al. “Avelumab: clinical trial innovation and collaboration to advance anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy” Annals of Oncology 2017, 28, 1659. 2. Jagoda et al. “Immuno-PET imaging of the programmed cell death-1 ligand (PD-L1) using the therapeutic mAb, Avelumab.” J. Nucl Med 2017, 58, sup. 1, 178 Funded by NCI Contract No. HHSN261200800001E