Abstract
1838
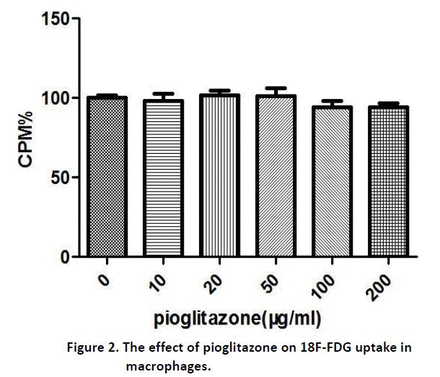
Introduction: To investigate the effects of pioglitazone on 18F-FDG uptake of A549 lung cancer cells and RAW264.7 macrophages. Method A549 lung cancer cells and RAW264.7 macrophages were treated with different concentrations of pioglitazone (10μg/ml, 20μg/ml, 50μg/ml, 100μg/ml and 200μg/ml) respectively for 1 hour, after that incubated with 18F-FDG for another 1 hour, then the change of 18F-FDG uptake in these cells was measured separately by a γ counter. Both types of cells were treated with 100μg/ml pioglitazone for 1 hour, next incubated with 18F-FDG for 1 hour, 2 hour, 3 hour, 4 hour, 5 hour and 6 hour,finally the variation of 18F-FDG uptake in these cells was measured separately by the γ counter at six different time points. Result 18F-FDG uptake of lung cancer cells in five different concentrations groups of pioglitazone were both higher than that in the blank control group(both P<0.05,figure 1). However, in macrophages, no significant difference was discovered in 18F-FDG uptake between the drug concentration 10μg/ml group, 20μg/ml group, 50μg/ml group and the blank control group respectively (both P>0.05), and 18F-FDG uptake in the dug concentration 100μg/ml group and 200μg/ml group were both lower than that in the blank control group (both P<0.05,figure 2). AT Six different time points, 18F-FDG uptake in the drug groups were both higher than that in the blank control group in lung cancer cells (both P<0.05,figure 3), whereas, compared with the control group, 18F-FDG uptake in the drug groups had no obvious changes in macrophages(both P>0.05,figure 4). Conclusion Pioglitazone can increase the 18F-FDG uptake of A549 lung cancer cells in short term, but make the 18F-FDG uptake of RAW264.7 macrophages unchanged or reduced.