Abstract
163
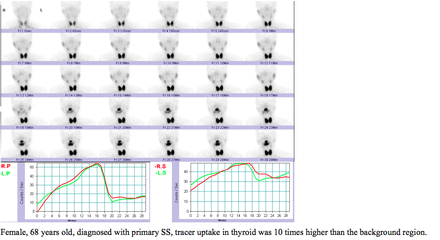
Objectives: In clinical work of salivary gland scintigraphy (SGS) interpretation, we sometimes encounter cases with diffusely increased tracer uptake in thyroid gland. As is known, both salivary glands and thyroid gland can be involved in autoimmune disease. This study aimed to investigate the correlation between serologic thyroid function tests and salivary function in the subject with increased accumulation in thyroid on Tc-99m pertechnetate scans. Methods: This study retrospectively reviewed 69 subjects who had a SGS in our institution from February 2013 to March 2017. SGS images were acquired into three image series (dynamic image, pre-syringe image and post-syringe image). The dynamic images were acquired immediately after a bolus injection of 370 MBq Tc-99m pertechnetate with 128x128 matrix, zoom 1.23, 60s/f x30 frames. The pre and post syringe images were acquired with a matrix size 256x256, zoom 1.0, and 6 sec. All these subjects included thyroid gland in the scan view and had serologic thyroid function tests. Those subjects were divided into 2 groups according to the tracer uptake intensity in thyroid: 34 cases (male 1, female 33, average age 49.3) were divided into experiment group (diffusely increased tracer uptake in thyroid gland, 10 times higher uptakes than the background region), and 35 cases (male 1, female 34, average age 53.4) with normal thyroid uptake were divided into control group. The indicators including the uptake ratio at 15 minute (UR15min) and the secretion rate (SR) after vitamin C stimulation at 20 minute were obtained from SGS. The correlation between the indicators and results of serum anti-thyroid autoantibodies including anti-thyroglobulin (Tg-Ab) and anti-peroxidase (TPO-Ab) was analyzed. The level of serum TPO-Ab and Tg-Ab in different groups was compared, too. Results: The primary diseases of the experiment and control groups were primary Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) (7/34 vs 12/35), secondary SS (16/34 vs 6/35) and other connective tissue diseases (4/34 vs 17/35). 52.9% (18/34) patients were diagnosed with autoimmune thyroid disease after the clue of increased uptake in thyroid on SGS. The percentage of patients with elevated Tg-Ab, TPO-Ab and both of them was 79.4% (27/34), 61.8% (21/34), and 58.8% (20/34) in experiment group respectively vs 34.3% (12/35), 17.1% (6/35), and 11.4% (4/35) in control group. The level of TG-Ab (U=282.5, p<0.05) and TPO-Ab (U=181.0, p<0.05) was significantly different in two groups, respectively. The SR value of right parotid gland and bilateral submandibular glands was negative correlated with the level of Tg-Ab (rp=-0.463, rrs=-0.503, rls=-0.462, p<0.05) and TPO-Ab (rp=-0.369, rrs=-0.416, rls=-0.373, p<0.05) in experiment group, and the UR15min of four glands was not correlated.
Conclusions: The secretion function after acid stimulation of salivary gland was negative correlated with the level of serum TPO-Ab and Tg-Ab in subjects with increased tracer uptake in thyroid gland on SGS.